48
.github/workflows/esp-idf_with-gfx.yml
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
|||
name: esp-idf with Adafruit GFX Library
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
paths-ignore:
|
||||
- '**.md'
|
||||
- 'doc/**'
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
paths-ignore:
|
||||
- '**.md'
|
||||
- 'doc/**'
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
build:
|
||||
name: esp-idf with Adafruit GFX
|
||||
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout repo
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
submodules: 'recursive'
|
||||
- name: Checkout ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA component
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: 'examples/esp-idf/with-gfx/components/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA'
|
||||
- name: Checkout Adafruit-GFX-Library repo
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
repository: 'adafruit/Adafruit-GFX-Library'
|
||||
path: 'examples/esp-idf/with-gfx/components/Adafruit-GFX-Library'
|
||||
- name: Checkout Adafruit_BusIO repo
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
repository: 'adafruit/Adafruit_BusIO'
|
||||
path: 'examples/esp-idf/with-gfx/components/Adafruit_BusIO'
|
||||
- name: Checkout arduino-esp32 repo
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
repository: 'espressif/arduino-esp32'
|
||||
path: 'examples/esp-idf/with-gfx/components/arduino'
|
||||
- name: esp-idf build
|
||||
uses: espressif/esp-idf-ci-action@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
esp_idf_version: v4.4.4
|
||||
target: esp32
|
||||
path: 'examples/esp-idf/with-gfx'
|
||||
33
.github/workflows/esp-idf_without-gfx.yml
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
|||
name: esp-idf without Adafruit GFX Library
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
paths-ignore:
|
||||
- '**.md'
|
||||
- 'doc/**'
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
paths-ignore:
|
||||
- '**.md'
|
||||
- 'doc/**'
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
build:
|
||||
name: esp-idf without Adafruit GFX
|
||||
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout repo
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
submodules: 'recursive'
|
||||
- name: Checkout ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA component
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: 'examples/esp-idf/without-gfx/components/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA'
|
||||
- name: esp-idf build
|
||||
uses: espressif/esp-idf-ci-action@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
esp_idf_version: v4.4
|
||||
target: esp32
|
||||
path: 'examples/esp-idf/without-gfx'
|
||||
18
.github/workflows/pio_build.yml
vendored
|
|
@ -10,13 +10,11 @@ on:
|
|||
paths-ignore:
|
||||
- '**.md'
|
||||
- 'doc/**'
|
||||
- '.github/**'
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
branches: [ master, dev ]
|
||||
paths-ignore:
|
||||
- '**.md'
|
||||
- 'doc/**'
|
||||
- '.github/**'
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
build:
|
||||
|
|
@ -26,18 +24,18 @@ jobs:
|
|||
matrix:
|
||||
framework: ["Arduino", "IDF"]
|
||||
no_gfx: ["", -DNO_GFX]
|
||||
no_fast_functions: ["", -DNO_FAST_FUNCTIONS]
|
||||
no_cie1931: ["", -DNO_CIE1931]
|
||||
virtual_panel: ["", -DVIRTUAL_PANE]
|
||||
# no_fast_functions: ["", -DNO_FAST_FUNCTIONS]
|
||||
# no_cie1931: ["", -DNO_CIE1931]
|
||||
# virtual_panel: ["", -DVIRTUAL_PANE]
|
||||
example:
|
||||
- "examples/PIO_TestPatterns"
|
||||
exclude:
|
||||
- no_fast_functions: ""
|
||||
virtual_panel: -DVIRTUAL_PANE
|
||||
# exclude:
|
||||
# - no_fast_functions: ""
|
||||
# virtual_panel: -DVIRTUAL_PANE
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- name: Cache pip and platformio
|
||||
uses: actions/cache@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
|
|
@ -50,7 +48,7 @@ jobs:
|
|||
with:
|
||||
python-version: '3.x'
|
||||
- name: Install Platformio
|
||||
run: pip install --upgrade platformio
|
||||
run: pip install --upgrade platformio==6.1.6
|
||||
- name: Run PlatformIO CI (Arduino)
|
||||
if: ${{ matrix.framework == 'Arduino'}}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -5,17 +5,34 @@
|
|||
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5)
|
||||
idf_build_get_property(target IDF_TARGET)
|
||||
|
||||
if(ARDUINO_ARCH_ESP32)
|
||||
list(APPEND arduino_build arduino Adafruit-GFX-Library)
|
||||
if(ARDUINO_ARCH_ESP32 OR CONFIG_ESP32_HUB75_USE_GFX)
|
||||
list(APPEND build_dependencies arduino Adafruit-GFX-Library)
|
||||
else()
|
||||
list(APPEND esp_idf_build esp_lcd driver)
|
||||
list(APPEND build_dependencies esp_lcd driver)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
idf_component_register(SRCS "src/platforms/esp32/esp32_i2s_parallel_dma.cpp" "src/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA.cpp" "src/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-leddrivers.cpp"
|
||||
src/platforms/${target}/gdma_lcd_parallel16.cpp
|
||||
INCLUDE_DIRS "./src"
|
||||
REQUIRES ${arduino_build} ${esp_idf_build}
|
||||
|
||||
if(${target} STREQUAL "esp32s3")
|
||||
list(APPEND extra_srcs src/platforms/${target}/gdma_lcd_parallel16.cpp)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
idf_component_register(SRCS "src/platforms/esp32/esp32_i2s_parallel_dma.cpp" "src/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA.cpp" "src/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-leddrivers.cpp" ${extra_srcs}
|
||||
INCLUDE_DIRS "./src"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Dependencies cannot be added to the REQUIRES argument of `idf_component_register` because (according to the build process
|
||||
# listed at https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/v4.2/esp32/api-guides/build-system.html#build-process)
|
||||
# `idf_component_register` is processed during the "Enumeration" stage which happens before the sdkconfig file is loaded
|
||||
# in the "Processing" stage. So if dependencies are going to be loaded based on certain CONFIG_* variables we must
|
||||
# use `target_link_libraries` instead. This is the method used by Arduino's CMakeLists.txt file.
|
||||
idf_build_get_property(components BUILD_COMPONENTS)
|
||||
foreach(component_name IN LISTS build_dependencies)
|
||||
if (NOT ${component_name} IN_LIST components)
|
||||
message(FATAL_ERROR "Missing component: ${component_name}")
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
idf_component_get_property(lib_name ${component_name} COMPONENT_LIB)
|
||||
target_link_libraries(${COMPONENT_LIB} PUBLIC ${lib_name})
|
||||
endforeach()
|
||||
|
||||
# In case you are running into issues with "missing" header files from 3rd party libraries
|
||||
# you can add them to the REQUIRES section above. If you use some of the build options below
|
||||
# you probably want to remove (NO_GFX) or replace Adafruit-GFX-Library (USE_GFX_ROOT)
|
||||
|
|
@ -25,11 +42,14 @@ idf_component_register(SRCS "src/platforms/esp32/esp32_i2s_parallel_dma.cpp" "sr
|
|||
# target_compile_options(${COMPONENT_TARGET} PUBLIC -DNO_GFX)
|
||||
|
||||
# esp-idf does not have any GFX library support yet, so we need to define NO_GFX
|
||||
if(ARDUINO_ARCH_ESP32)
|
||||
if(ARDUINO_ARCH_ESP32 OR CONFIG_ESP32_HUB75_USE_GFX)
|
||||
else()
|
||||
target_compile_options(${COMPONENT_TARGET} PUBLIC -DNO_GFX)
|
||||
if(${target} STREQUAL "esp32s3")
|
||||
target_compile_options(${COMPONENT_TARGET} PUBLIC -DSPIRAM_FRAMEBUFFER)
|
||||
# Don't enable PSRAM based framebuffer just because it's an S3.
|
||||
# This is an advanced option and should only be used with an S3 with Octal-SPI RAM.
|
||||
# target_compile_options(${COMPONENT_TARGET} PUBLIC -DSPIRAM_FRAMEBUFFER)
|
||||
target_compile_options(${COMPONENT_TARGET} PUBLIC)
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
endif()
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
9
Kconfig.projbuild
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
|||
menu "ESP32 HUB75 Configuration"
|
||||
|
||||
config ESP32_HUB75_USE_GFX
|
||||
bool "Use Adafruit GFX library."
|
||||
default y
|
||||
help
|
||||
This option enables use of the Adafruit GFX library using the `Adafruit-GFX-Library` component.
|
||||
|
||||
endmenu
|
||||
14
README.md
|
|
@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ A typical 64x32px panel at 24bpp colour uses about 20kB of internal memory.
|
|||
|
||||
Please use the ['Memory Calculator'](/doc/memcalc.md) to see what is *typically* achievable with the typical ESP32. 
|
||||
|
||||
For the ESP32-S3 only, you can use SPIRAM/PSRAM to drive the HUB75 DMA buffer when using **Octal SPI-RAM** (i.e. ESP32 S3 N8R8 variant). However, due to bandwidth limitations, the maximum output frequency is limited to approx. 13Mhz, which will limit the real-world number of panels that can be chained without flicker.
|
||||
For the ESP32-S3 only, you can use SPIRAM/PSRAM to drive the HUB75 DMA buffer when using an ESP32-S3 with **OCTAL SPI-RAM (PSTRAM)** (i.e. ESP32 S3 N8R8 variant). However, due to bandwidth limitations, the maximum output frequency is limited to approx. 13Mhz, which will limit the real-world number of panels that can be chained without flicker. Please do not use PSRAM as the DMA buffer if using QUAD SPI (Q-SPI), as it's too slow.
|
||||
|
||||
To enable PSRAM support on the ESP32-S3, refer to [the build options](/doc/BuildOptions.md) to enable.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -82,9 +82,11 @@ Due to the high-speed optimized nature of this library, only specific panels are
|
|||
* ICND2012
|
||||
* [RUC7258](http://www.ruichips.com/en/products.html?cateid=17496)
|
||||
* FM6126A AKA ICN2038S, [FM6124](https://datasheet4u.com/datasheet-pdf/FINEMADELECTRONICS/FM6124/pdf.php?id=1309677) (Refer to [PatternPlasma](/examples/2_PatternPlasma) example on how to use.)
|
||||
* SM5266P
|
||||
* SM5266P
|
||||
* DP3246 with SM5368 row addressing registers
|
||||
|
||||
## Unsupported Panels
|
||||
## Unsupported chips
|
||||
* [SM1620B](https://github.com/mrfaptastic/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-DMA/issues/416)
|
||||
* RUL5358 / SHIFTREG_ABC_BIN_DE based panels are not supported.
|
||||
* ICN2053 / FM6353 based panels - Refer to [this library](https://github.com/LAutour/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-DMA-ICN2053), which is a fork of this library ( [discussion link](https://github.com/mrfaptastic/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-DMA/discussions/324)).
|
||||
* Any other panel not listed above.
|
||||
|
|
@ -94,7 +96,7 @@ Please use an [alternative library](https://github.com/2dom/PxMatrix) if you bou
|
|||
# Getting Started
|
||||
## 1. Library Installation
|
||||
|
||||
* Dependancy: You will need to install Adafruit_GFX from the "Library > Manage Libraries" menu.
|
||||
* Dependency: You will need to install Adafruit_GFX from the "Library > Manage Libraries" menu.
|
||||
* Install this library from the Arduino Library manager.
|
||||
|
||||
Library also tested to work fine with PlatformIO, install into your PlatformIO projects' lib/ folder as appropriate. Or just add it into [platformio.ini](/doc/BuildOptions.md) [lib_deps](https://docs.platformio.org/en/latest/projectconf/section_env_library.html#lib-deps) section.
|
||||
|
|
@ -132,6 +134,8 @@ HUB75_I2S_CFG mxconfig(
|
|||
dma_display = new MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA(mxconfig);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure you also connect one of the HUB75 interfaces ground pins to a ground pin of the ESP32, otherwise you may get electrical artefacts on LED Matrix Panel.
|
||||
|
||||
Various people have created PCBs for which one can simply connect an ESP32 to a PCB, and then the PCB to the HUB75 connector, such as:
|
||||
|
||||
* Brian Lough's [ESP32 I2S Matrix Shield](http://blough.ie/i2smat/)
|
||||
|
|
@ -226,4 +230,6 @@ There are a number of great looking LED graphical display projects which leverag
|
|||
* [PaintYourDragon](https://github.com/PaintYourDragon) for the DMA logic for the ESP32-S3.
|
||||
* And lots of others, let me know if I've missed you.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to donate money to the project, please refer to [this discussion](https://github.com/mrfaptastic/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-DMA/discussions/349) about it. If you want to donate/buy an LED panel for the library author to improve compatibility and/or testing - please feel free to post in the same [discussion](https://github.com/mrfaptastic/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-DMA/discussions/349).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
|
|
|||
BIN
doc/Panel_Chaining_Types.ods
Normal file
BIN
doc/VirtualMatrixPanel.odp
Normal file
BIN
doc/VirtualMatrixPanel.pdf
Normal file
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,9 @@
|
|||
// Example uses the following configuration: mxconfig.double_buff = true;
|
||||
// to enable double buffering, which means display->flipDMABuffer(); is required.
|
||||
|
||||
// Bounce squares around the screen, doing the re-drawing in the background back-buffer.
|
||||
// Double buffering is not always required in reality.
|
||||
|
||||
#include <ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA.h>
|
||||
|
||||
MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA *display = nullptr;
|
||||
|
|
@ -32,14 +38,14 @@ void setup()
|
|||
|
||||
Serial.println("...Starting Display");
|
||||
HUB75_I2S_CFG mxconfig;
|
||||
//mxconfig.double_buff = true; // Turn of double buffer
|
||||
mxconfig.clkphase = false;
|
||||
mxconfig.double_buff = true; // <------------- Turn on double buffer
|
||||
//mxconfig.clkphase = false;
|
||||
|
||||
// OK, now we can create our matrix object
|
||||
display = new MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA(mxconfig);
|
||||
display->begin(); // setup display with pins as pre-defined in the library
|
||||
|
||||
// Create some Squares
|
||||
// Create some random squares
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < numSquares; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
Squares[i].square_size = random(2,10);
|
||||
|
|
@ -47,8 +53,6 @@ void setup()
|
|||
Squares[i].ypos = random(0, display->height() - Squares[i].square_size);
|
||||
Squares[i].velocityx = static_cast <float> (rand()) / static_cast <float> (RAND_MAX);
|
||||
Squares[i].velocityy = static_cast <float> (rand()) / static_cast <float> (RAND_MAX);
|
||||
//Squares[i].xdir = (random(2) == 1) ? true:false;
|
||||
//Squares[i].ydir = (random(2) == 1) ? true:false;
|
||||
|
||||
int random_num = random(6);
|
||||
Squares[i].colour = colours[random_num];
|
||||
|
|
@ -57,9 +61,11 @@ void setup()
|
|||
|
||||
void loop()
|
||||
{
|
||||
display->flipDMABuffer(); // not used if double buffering isn't enabled
|
||||
delay(25);
|
||||
display->clearScreen();
|
||||
|
||||
display->flipDMABuffer(); // Show the back buffer, set currently output buffer to the back (i.e. no longer being sent to LED panels)
|
||||
display->clearScreen(); // Now clear the back-buffer
|
||||
|
||||
delay(16); // <----------- Shouldn't see this clearscreen occur as it happens on the back buffer when double buffering is enabled.
|
||||
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < numSquares; i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
|
|||
## FM6126 based LED Matrix Panel Reset ##
|
||||
|
||||
FM6216 panels require a special reset sequence before they can be used, check your panel chipset if you have issues. Refer to this example.
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,19 +1,30 @@
|
|||
// How to use this library with a FM6126 panel, thanks goes to:
|
||||
// https://github.com/hzeller/rpi-rgb-led-matrix/issues/746
|
||||
/**********************************************************************
|
||||
* The library by default supports simple 'shift register' based panels
|
||||
* with A,B,C,D,E lines to select a specific row, but there are plenty
|
||||
* of examples of new chips coming on the market that work different.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Please search through the project's issues. For some of these chips
|
||||
* (you will need to look at the back of your panel to identify), this
|
||||
* library has workarounds. This can be configured through using one of:
|
||||
|
||||
// mxconfig.driver = HUB75_I2S_CFG::FM6126A;
|
||||
//mxconfig.driver = HUB75_I2S_CFG::ICN2038S;
|
||||
//mxconfig.driver = HUB75_I2S_CFG::FM6124;
|
||||
//mxconfig.driver = HUB75_I2S_CFG::MBI5124;
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#include <Arduino.h>
|
||||
#include <ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA.h>
|
||||
#include <FastLED.h>
|
||||
|
||||
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
|
||||
// FM6126 support is still experimental
|
||||
|
||||
// Output resolution and panel chain length configuration
|
||||
#define PANEL_RES_X 64 // Number of pixels wide of each INDIVIDUAL panel module.
|
||||
#define PANEL_RES_Y 32 // Number of pixels tall of each INDIVIDUAL panel module.
|
||||
#define PANEL_CHAIN 1 // Total number of panels chained one to another
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// placeholder for the matrix object
|
||||
MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA *dma_display = nullptr;
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -33,14 +44,6 @@ CRGB ColorFromCurrentPalette(uint8_t index = 0, uint8_t brightness = 255, TBlend
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void setup(){
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
The configuration for MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA object is held in HUB75_I2S_CFG structure,
|
||||
All options has it's predefined default values. So we can create a new structure and redefine only the options we need
|
||||
|
||||
Please refer to the '2_PatternPlasma.ino' example for detailed example of how to use the MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA configuration
|
||||
if you need to change the pin mappings etc.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
HUB75_I2S_CFG mxconfig(
|
||||
PANEL_RES_X, // module width
|
||||
|
|
@ -48,7 +51,12 @@ void setup(){
|
|||
PANEL_CHAIN // Chain length
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
mxconfig.driver = HUB75_I2S_CFG::FM6126A; // in case that we use panels based on FM6126A chip, we can set it here before creating MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA object
|
||||
// in case that we use panels based on FM6126A chip, we can set it here before creating MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA object
|
||||
mxconfig.driver = HUB75_I2S_CFG::FM6126A;
|
||||
//mxconfig.driver = HUB75_I2S_CFG::ICN2038S;
|
||||
//mxconfig.driver = HUB75_I2S_CFG::FM6124;
|
||||
//mxconfig.driver = HUB75_I2S_CFG::MBI5124;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// OK, now we can create our matrix object
|
||||
dma_display = new MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA(mxconfig);
|
||||
|
|
@ -99,4 +107,8 @@ void loop(){
|
|||
fps_timer = millis();
|
||||
fps = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// FM6126 panel , thanks goes to:
|
||||
// https://github.com/hzeller/rpi-rgb-led-matrix/issues/746
|
||||
13
examples/4_OtherShiftDriverPanel/README.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
|||
## Ohter driver based LED Matrix Panels ##
|
||||
|
||||
Limited support for other panels exists, but requires this to be passed as a configuration option when using the library.
|
||||
|
||||
These panels require a special reset sequence before they can be used, check your panel chipset if you have issues. Refer to the example.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mxconfig.driver = HUB75_I2S_CFG::FM6126A;
|
||||
mxconfig.driver = HUB75_I2S_CFG::ICN2038S;
|
||||
mxconfig.driver = HUB75_I2S_CFG::FM6124;
|
||||
mxconfig.driver = HUB75_I2S_CFG::MBI5124;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,7 +0,0 @@
|
|||
// Example sketch which shows how to display a 64x32 animated GIF image stored in FLASH memory
|
||||
// on a 64x32 LED matrix
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Credits: https://github.com/bitbank2/AnimatedGIF/tree/master/examples/ESP32_LEDMatrix_I2S
|
||||
//
|
||||
|
||||
// Refer to: https://github.com/bitbank2/AnimatedGIF/blob/master/examples/ESP32_LEDMatrix_I2S/ESP32_LEDMatrix_I2S.ino
|
||||
268
examples/AnimatedGIFPanel_SD/AnimatedGIFPanel_SD.ino
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,268 @@
|
|||
/*********************************************************************
|
||||
* AnimatedGif LED Matrix Panel example where the GIFs are
|
||||
* stored on a SD card connected to the ESP32 using the
|
||||
* standard GPIO pins used for SD card acces via. SPI.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Put the gifs into a directory called 'gifs' (case sensitive) on
|
||||
* a FAT32 formatted SDcard.
|
||||
********************************************************************/
|
||||
#include "FS.h"
|
||||
#include "SD.h"
|
||||
#include "SPI.h"
|
||||
#include <ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA.h>
|
||||
#include <AnimatedGIF.h>
|
||||
|
||||
/********************************************************************
|
||||
* Pin mapping below is for LOLIN D32 (ESP 32)
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Default pin mapping used by this library is NOT compatable with the use of the
|
||||
* ESP32-Arduino 'SD' card library (there is overlap). As such, some of the pins
|
||||
* used for the HUB75 panel need to be shifted.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* 'SD' card library requires GPIO 23, 18 and 19
|
||||
* https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/tree/master/libraries/SD
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Connect the SD card to the following pins:
|
||||
*
|
||||
* SD Card | ESP32
|
||||
* D2 -
|
||||
* D3 SS
|
||||
* CMD MOSI
|
||||
* VSS GND
|
||||
* VDD 3.3V
|
||||
* CLK SCK
|
||||
* VSS GND
|
||||
* D0 MISO
|
||||
* D1 -
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/**** SD Card GPIO mappings ****/
|
||||
#define SS_PIN 5
|
||||
//#define MOSI_PIN 23
|
||||
//#define MISO_PIN 19
|
||||
//#define CLK_PIN 18
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**** HUB75 GPIO mapping ****/
|
||||
// GPIO 34+ are on the ESP32 are input only!!
|
||||
// https://randomnerdtutorials.com/esp32-pinout-reference-gpios/
|
||||
|
||||
#define A_PIN 33 // remap esp32 library default from 23 to 33
|
||||
#define B_PIN 32 // remap esp32 library default from 19 to 32
|
||||
#define C_PIN 22 // remap esp32 library defaultfrom 5 to 22
|
||||
|
||||
//#define R1_PIN 25 // library default for the esp32, unchanged
|
||||
//#define G1_PIN 26 // library default for the esp32, unchanged
|
||||
//#define B1_PIN 27 // library default for the esp32, unchanged
|
||||
//#define R2_PIN 14 // library default for the esp32, unchanged
|
||||
//#define G2_PIN 12 // library default for the esp32, unchanged
|
||||
//#define B2_PIN 13 // library default for the esp32, unchanged
|
||||
//#define D_PIN 17 // library default for the esp32, unchanged
|
||||
//#define E_PIN -1 // IMPORTANT: Change to a valid pin if using a 64x64px panel.
|
||||
|
||||
//#define LAT_PIN 4 // library default for the esp32, unchanged
|
||||
//#define OE_PIN 15 // library default for the esp32, unchanged
|
||||
//#define CLK_PIN 16 // library default for the esp32, unchanged
|
||||
|
||||
/***************************************************************
|
||||
* HUB 75 LED DMA Matrix Panel Configuration
|
||||
**************************************************************/
|
||||
#define PANEL_RES_X 64 // Number of pixels wide of each INDIVIDUAL panel module.
|
||||
#define PANEL_RES_Y 32 // Number of pixels tall of each INDIVIDUAL panel module.
|
||||
#define PANEL_CHAIN 1 // Total number of panels chained one to another
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************/
|
||||
|
||||
AnimatedGIF gif;
|
||||
MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA *dma_display = nullptr;
|
||||
|
||||
static int totalFiles = 0; // GIF files count
|
||||
|
||||
static File FSGifFile; // temp gif file holder
|
||||
static File GifRootFolder; // directory listing
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<std::string> GifFiles; // GIF files path
|
||||
|
||||
const int maxGifDuration = 30000; // ms, max GIF duration
|
||||
|
||||
#include "gif_functions.hpp"
|
||||
#include "sdcard_functions.hpp"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/**************************************************************/
|
||||
void draw_test_patterns();
|
||||
int gifPlay( const char* gifPath )
|
||||
{ // 0=infinite
|
||||
|
||||
if( ! gif.open( gifPath, GIFOpenFile, GIFCloseFile, GIFReadFile, GIFSeekFile, GIFDraw ) ) {
|
||||
log_n("Could not open gif %s", gifPath );
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.print("Playing: "); Serial.println(gifPath);
|
||||
|
||||
int frameDelay = 0; // store delay for the last frame
|
||||
int then = 0; // store overall delay
|
||||
|
||||
while (gif.playFrame(true, &frameDelay)) {
|
||||
|
||||
then += frameDelay;
|
||||
if( then > maxGifDuration ) { // avoid being trapped in infinite GIF's
|
||||
//log_w("Broke the GIF loop, max duration exceeded");
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
gif.close();
|
||||
|
||||
return then;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void setup()
|
||||
{
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
|
||||
// **************************** Setup SD Card access via SPI ****************************
|
||||
if(!SD.begin(SS_PIN)){
|
||||
// bool begin(uint8_t ssPin=SS, SPIClass &spi=SPI, uint32_t frequency=4000000, const char * mountpoint="/sd", uint8_t max_files=5, bool format_if_empty=false);
|
||||
Serial.println("Card Mount Failed");
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
uint8_t cardType = SD.cardType();
|
||||
|
||||
if(cardType == CARD_NONE){
|
||||
Serial.println("No SD card attached");
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.print("SD Card Type: ");
|
||||
if(cardType == CARD_MMC){
|
||||
Serial.println("MMC");
|
||||
} else if(cardType == CARD_SD){
|
||||
Serial.println("SDSC");
|
||||
} else if(cardType == CARD_SDHC){
|
||||
Serial.println("SDHC");
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
Serial.println("UNKNOWN");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
uint64_t cardSize = SD.cardSize() / (1024 * 1024);
|
||||
Serial.printf("SD Card Size: %lluMB\n", cardSize);
|
||||
|
||||
//listDir(SD, "/", 1, false);
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.printf("Total space: %lluMB\n", SD.totalBytes() / (1024 * 1024));
|
||||
Serial.printf("Used space: %lluMB\n", SD.usedBytes() / (1024 * 1024));
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// **************************** Setup DMA Matrix ****************************
|
||||
HUB75_I2S_CFG mxconfig(
|
||||
PANEL_RES_X, // module width
|
||||
PANEL_RES_Y, // module height
|
||||
PANEL_CHAIN // Chain length
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
// Need to remap these HUB75 DMA pins because the SPI SDCard is using them.
|
||||
// Otherwise the SD Card will not work.
|
||||
mxconfig.gpio.a = A_PIN;
|
||||
mxconfig.gpio.b = B_PIN;
|
||||
mxconfig.gpio.c = C_PIN;
|
||||
// mxconfig.gpio.d = D_PIN;
|
||||
|
||||
//mxconfig.clkphase = false;
|
||||
//mxconfig.driver = HUB75_I2S_CFG::FM6126A;
|
||||
|
||||
// Display Setup
|
||||
dma_display = new MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA(mxconfig);
|
||||
|
||||
// Allocate memory and start DMA display
|
||||
if( not dma_display->begin() )
|
||||
Serial.println("****** !KABOOM! HUB75 memory allocation failed ***********");
|
||||
|
||||
dma_display->setBrightness8(128); //0-255
|
||||
dma_display->clearScreen();
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// **************************** Setup Sketch ****************************
|
||||
Serial.println("Starting AnimatedGIFs Sketch");
|
||||
|
||||
// SD CARD STOPS WORKING WITH DMA DISPLAY ENABLED>...
|
||||
|
||||
File root = SD.open("/gifs");
|
||||
if(!root){
|
||||
Serial.println("Failed to open directory");
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
File file = root.openNextFile();
|
||||
while(file){
|
||||
if(!file.isDirectory())
|
||||
{
|
||||
Serial.print(" FILE: ");
|
||||
Serial.print(file.name());
|
||||
Serial.print(" SIZE: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(file.size());
|
||||
|
||||
std::string filename = "/gifs/" + std::string(file.name());
|
||||
Serial.println(filename.c_str());
|
||||
|
||||
GifFiles.push_back( filename );
|
||||
// Serial.println("Adding to gif list:" + String(filename));
|
||||
totalFiles++;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
file = root.openNextFile();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
file.close();
|
||||
Serial.printf("Found %d GIFs to play.", totalFiles);
|
||||
//totalFiles = getGifInventory("/gifs");
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// This is important - Set the right endianness.
|
||||
gif.begin(LITTLE_ENDIAN_PIXELS);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop(){
|
||||
|
||||
// Iterate over a vector using range based for loop
|
||||
for(auto & elem : GifFiles)
|
||||
{
|
||||
gifPlay( elem.c_str() );
|
||||
gif.reset();
|
||||
delay(500);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void draw_test_patterns()
|
||||
{
|
||||
// fix the screen with green
|
||||
dma_display->fillRect(0, 0, dma_display->width(), dma_display->height(), dma_display->color444(0, 15, 0));
|
||||
delay(500);
|
||||
|
||||
// draw a box in yellow
|
||||
dma_display->drawRect(0, 0, dma_display->width(), dma_display->height(), dma_display->color444(15, 15, 0));
|
||||
delay(500);
|
||||
|
||||
// draw an 'X' in red
|
||||
dma_display->drawLine(0, 0, dma_display->width()-1, dma_display->height()-1, dma_display->color444(15, 0, 0));
|
||||
dma_display->drawLine(dma_display->width()-1, 0, 0, dma_display->height()-1, dma_display->color444(15, 0, 0));
|
||||
delay(500);
|
||||
|
||||
// draw a blue circle
|
||||
dma_display->drawCircle(10, 10, 10, dma_display->color444(0, 0, 15));
|
||||
delay(500);
|
||||
|
||||
// fill a violet circle
|
||||
dma_display->fillCircle(40, 21, 10, dma_display->color444(15, 0, 15));
|
||||
delay(500);
|
||||
delay(1000);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
15
examples/AnimatedGIFPanel_SD/Readme.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
|||
# ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-DMA SDCard example
|
||||
|
||||
A very basic example using the 'Animated GIF' library by Larry Bank + the SD / File system library provided for Arduino by Espressif.
|
||||
|
||||
Some default HUB75 pins need to be remapped to accomodate for the SD Card.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## How to use it?
|
||||
|
||||
1. Format a SD Card with FAT32 file system (default setting)
|
||||
2. Create a directory called 'gifs'
|
||||
3. Drop your gifs in there. The resolution of the GIFS must match that of the display.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
BIN
examples/AnimatedGIFPanel_SD/esp32_sdcard.jpg
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 150 KiB |
132
examples/AnimatedGIFPanel_SD/gif_functions.hpp
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
|
|||
|
||||
// Code copied from AnimatedGIF examples
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef M5STACK_SD
|
||||
// for custom ESP32 builds
|
||||
#define M5STACK_SD SD
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
static void * GIFOpenFile(const char *fname, int32_t *pSize)
|
||||
{
|
||||
//log_d("GIFOpenFile( %s )\n", fname );
|
||||
FSGifFile = M5STACK_SD.open(fname);
|
||||
if (FSGifFile) {
|
||||
*pSize = FSGifFile.size();
|
||||
return (void *)&FSGifFile;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
static void GIFCloseFile(void *pHandle)
|
||||
{
|
||||
File *f = static_cast<File *>(pHandle);
|
||||
if (f != NULL)
|
||||
f->close();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
static int32_t GIFReadFile(GIFFILE *pFile, uint8_t *pBuf, int32_t iLen)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int32_t iBytesRead;
|
||||
iBytesRead = iLen;
|
||||
File *f = static_cast<File *>(pFile->fHandle);
|
||||
// Note: If you read a file all the way to the last byte, seek() stops working
|
||||
if ((pFile->iSize - pFile->iPos) < iLen)
|
||||
iBytesRead = pFile->iSize - pFile->iPos - 1; // <-- ugly work-around
|
||||
if (iBytesRead <= 0)
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
iBytesRead = (int32_t)f->read(pBuf, iBytesRead);
|
||||
pFile->iPos = f->position();
|
||||
return iBytesRead;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
static int32_t GIFSeekFile(GIFFILE *pFile, int32_t iPosition)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i = micros();
|
||||
File *f = static_cast<File *>(pFile->fHandle);
|
||||
f->seek(iPosition);
|
||||
pFile->iPos = (int32_t)f->position();
|
||||
i = micros() - i;
|
||||
//log_d("Seek time = %d us\n", i);
|
||||
return pFile->iPos;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Draw a line of image directly on the LCD
|
||||
void GIFDraw(GIFDRAW *pDraw)
|
||||
{
|
||||
uint8_t *s;
|
||||
uint16_t *d, *usPalette, usTemp[320];
|
||||
int x, y, iWidth;
|
||||
|
||||
iWidth = pDraw->iWidth;
|
||||
if (iWidth > PANEL_RES_X)
|
||||
iWidth = PANEL_RES_X;
|
||||
usPalette = pDraw->pPalette;
|
||||
y = pDraw->iY + pDraw->y; // current line
|
||||
|
||||
s = pDraw->pPixels;
|
||||
if (pDraw->ucDisposalMethod == 2) {// restore to background color
|
||||
for (x=0; x<iWidth; x++) {
|
||||
if (s[x] == pDraw->ucTransparent)
|
||||
s[x] = pDraw->ucBackground;
|
||||
}
|
||||
pDraw->ucHasTransparency = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Apply the new pixels to the main image
|
||||
if (pDraw->ucHasTransparency) { // if transparency used
|
||||
uint8_t *pEnd, c, ucTransparent = pDraw->ucTransparent;
|
||||
int x, iCount;
|
||||
pEnd = s + iWidth;
|
||||
x = 0;
|
||||
iCount = 0; // count non-transparent pixels
|
||||
while(x < iWidth) {
|
||||
c = ucTransparent-1;
|
||||
d = usTemp;
|
||||
while (c != ucTransparent && s < pEnd) {
|
||||
c = *s++;
|
||||
if (c == ucTransparent) { // done, stop
|
||||
s--; // back up to treat it like transparent
|
||||
} else { // opaque
|
||||
*d++ = usPalette[c];
|
||||
iCount++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // while looking for opaque pixels
|
||||
if (iCount) { // any opaque pixels?
|
||||
for(int xOffset = 0; xOffset < iCount; xOffset++ ){
|
||||
dma_display->drawPixel(x + xOffset, y, usTemp[xOffset]); // 565 Color Format
|
||||
}
|
||||
x += iCount;
|
||||
iCount = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// no, look for a run of transparent pixels
|
||||
c = ucTransparent;
|
||||
while (c == ucTransparent && s < pEnd) {
|
||||
c = *s++;
|
||||
if (c == ucTransparent)
|
||||
iCount++;
|
||||
else
|
||||
s--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (iCount) {
|
||||
x += iCount; // skip these
|
||||
iCount = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
s = pDraw->pPixels;
|
||||
// Translate the 8-bit pixels through the RGB565 palette (already byte reversed)
|
||||
for (x=0; x<iWidth; x++)
|
||||
dma_display->drawPixel(x, y, usPalette[*s++]); // color 565
|
||||
/*
|
||||
usTemp[x] = usPalette[*s++];
|
||||
|
||||
for (x=0; x<pDraw->iWidth; x++) {
|
||||
dma_display->drawPixel(x, y, usTemp[*s++]); // color 565
|
||||
} */
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
} /* GIFDraw() */
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 29 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 29 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 44 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 44 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 39 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 39 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 171 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 171 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 58 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 58 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 31 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 31 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 34 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 34 KiB |
102
examples/AnimatedGIFPanel_SD/sdcard_functions.hpp
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
|
|||
/************************ SD Card Code ************************/
|
||||
// As per: https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32/tree/master/libraries/SD/examples/SD_Test
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void listDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * dirname, uint8_t levels, bool add_to_gif_list = false){
|
||||
Serial.printf("Listing directory: %s\n", dirname);
|
||||
|
||||
File root = fs.open(dirname);
|
||||
if(!root){
|
||||
Serial.println("Failed to open directory");
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if(!root.isDirectory()){
|
||||
Serial.println("Not a directory");
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
File file = root.openNextFile();
|
||||
while(file){
|
||||
if(file.isDirectory()){
|
||||
Serial.print(" DIR : ");
|
||||
Serial.println(file.name());
|
||||
if(levels){
|
||||
listDir(fs, file.path(), levels -1, false);
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
Serial.print(" FILE: ");
|
||||
Serial.print(file.name());
|
||||
Serial.print(" SIZE: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(file.size());
|
||||
|
||||
if (add_to_gif_list && levels == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
GifFiles.push_back( std::string(dirname) + file.name() );
|
||||
Serial.println("Adding to gif list:" + String(dirname) +"/" + file.name());
|
||||
totalFiles++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
file = root.openNextFile();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
file.close();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void readFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
|
||||
Serial.printf("Reading file: %s\n", path);
|
||||
|
||||
File file = fs.open(path);
|
||||
if(!file){
|
||||
Serial.println("Failed to open file for reading");
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.print("Read from file: ");
|
||||
while(file.available()){
|
||||
Serial.write(file.read());
|
||||
}
|
||||
file.close();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void testFileIO(fs::FS &fs, const char * path){
|
||||
File file = fs.open(path);
|
||||
static uint8_t buf[512];
|
||||
size_t len = 0;
|
||||
uint32_t start = millis();
|
||||
uint32_t end = start;
|
||||
if(file){
|
||||
len = file.size();
|
||||
size_t flen = len;
|
||||
start = millis();
|
||||
while(len){
|
||||
size_t toRead = len;
|
||||
if(toRead > 512){
|
||||
toRead = 512;
|
||||
}
|
||||
file.read(buf, toRead);
|
||||
len -= toRead;
|
||||
}
|
||||
end = millis() - start;
|
||||
Serial.printf("%u bytes read for %u ms\n", flen, end);
|
||||
file.close();
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
Serial.println("Failed to open file for reading");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
file = fs.open(path, FILE_WRITE);
|
||||
if(!file){
|
||||
Serial.println("Failed to open file for writing");
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
size_t i;
|
||||
start = millis();
|
||||
for(i=0; i<2048; i++){
|
||||
file.write(buf, 512);
|
||||
}
|
||||
end = millis() - start;
|
||||
Serial.printf("%u bytes written for %u ms\n", 2048 * 512, end);
|
||||
file.close();
|
||||
}
|
||||
290
examples/AnimatedGIFPanel_SPIFFS/AnimatedGIFPanel_SPIFFS.ino
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,290 @@
|
|||
// Example sketch which shows how to display a 64x32 animated GIF image stored in FLASH memory
|
||||
// on a 64x32 LED matrix
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Credits: https://github.com/bitbank2/AnimatedGIF/tree/master/examples/ESP32_LEDMatrix_I2S
|
||||
//
|
||||
|
||||
/* INSTRUCTIONS
|
||||
*
|
||||
* 1. First Run the 'ESP32 Sketch Data Upload Tool' in Arduino from the 'Tools' Menu.
|
||||
* - If you don't know what this is or see it as an option, then read this:
|
||||
* https://github.com/me-no-dev/arduino-esp32fs-plugin
|
||||
* - This tool will upload the contents of the data/ directory in the sketch folder onto
|
||||
* the ESP32 itself.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* 2. You can drop any animated GIF you want in there, but keep it to the resolution of the
|
||||
* MATRIX you're displaying to. To resize a gif, use this online website: https://ezgif.com/
|
||||
*
|
||||
* 3. Have fun.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#define FILESYSTEM SPIFFS
|
||||
#include <SPIFFS.h>
|
||||
#include <AnimatedGIF.h>
|
||||
#include <ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA.h>
|
||||
|
||||
// ----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
* Below is an is the 'legacy' way of initialising the MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA class.
|
||||
* i.e. MATRIX_WIDTH and MATRIX_HEIGHT are modified by compile-time directives.
|
||||
* By default the library assumes a single 64x32 pixel panel is connected.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Refer to the example '2_PatternPlasma' on the new / correct way to setup this library
|
||||
* for different resolutions / panel chain lengths within the sketch 'setup()'.
|
||||
*
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
#define PANEL_RES_X 64 // Number of pixels wide of each INDIVIDUAL panel module.
|
||||
#define PANEL_RES_Y 32 // Number of pixels tall of each INDIVIDUAL panel module.
|
||||
#define PANEL_CHAIN 1 // Total number of panels chained one to another
|
||||
|
||||
//MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA dma_display;
|
||||
MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA *dma_display = nullptr;
|
||||
|
||||
uint16_t myBLACK = dma_display->color565(0, 0, 0);
|
||||
uint16_t myWHITE = dma_display->color565(255, 255, 255);
|
||||
uint16_t myRED = dma_display->color565(255, 0, 0);
|
||||
uint16_t myGREEN = dma_display->color565(0, 255, 0);
|
||||
uint16_t myBLUE = dma_display->color565(0, 0, 255);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
AnimatedGIF gif;
|
||||
File f;
|
||||
int x_offset, y_offset;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Draw a line of image directly on the LED Matrix
|
||||
void GIFDraw(GIFDRAW *pDraw)
|
||||
{
|
||||
uint8_t *s;
|
||||
uint16_t *d, *usPalette, usTemp[320];
|
||||
int x, y, iWidth;
|
||||
|
||||
iWidth = pDraw->iWidth;
|
||||
if (iWidth > MATRIX_WIDTH)
|
||||
iWidth = MATRIX_WIDTH;
|
||||
|
||||
usPalette = pDraw->pPalette;
|
||||
y = pDraw->iY + pDraw->y; // current line
|
||||
|
||||
s = pDraw->pPixels;
|
||||
if (pDraw->ucDisposalMethod == 2) // restore to background color
|
||||
{
|
||||
for (x=0; x<iWidth; x++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (s[x] == pDraw->ucTransparent)
|
||||
s[x] = pDraw->ucBackground;
|
||||
}
|
||||
pDraw->ucHasTransparency = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// Apply the new pixels to the main image
|
||||
if (pDraw->ucHasTransparency) // if transparency used
|
||||
{
|
||||
uint8_t *pEnd, c, ucTransparent = pDraw->ucTransparent;
|
||||
int x, iCount;
|
||||
pEnd = s + pDraw->iWidth;
|
||||
x = 0;
|
||||
iCount = 0; // count non-transparent pixels
|
||||
while(x < pDraw->iWidth)
|
||||
{
|
||||
c = ucTransparent-1;
|
||||
d = usTemp;
|
||||
while (c != ucTransparent && s < pEnd)
|
||||
{
|
||||
c = *s++;
|
||||
if (c == ucTransparent) // done, stop
|
||||
{
|
||||
s--; // back up to treat it like transparent
|
||||
}
|
||||
else // opaque
|
||||
{
|
||||
*d++ = usPalette[c];
|
||||
iCount++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // while looking for opaque pixels
|
||||
if (iCount) // any opaque pixels?
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(int xOffset = 0; xOffset < iCount; xOffset++ ){
|
||||
dma_display->drawPixel(x + xOffset, y, usTemp[xOffset]); // 565 Color Format
|
||||
}
|
||||
x += iCount;
|
||||
iCount = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// no, look for a run of transparent pixels
|
||||
c = ucTransparent;
|
||||
while (c == ucTransparent && s < pEnd)
|
||||
{
|
||||
c = *s++;
|
||||
if (c == ucTransparent)
|
||||
iCount++;
|
||||
else
|
||||
s--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (iCount)
|
||||
{
|
||||
x += iCount; // skip these
|
||||
iCount = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
else // does not have transparency
|
||||
{
|
||||
s = pDraw->pPixels;
|
||||
// Translate the 8-bit pixels through the RGB565 palette (already byte reversed)
|
||||
for (x=0; x<pDraw->iWidth; x++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
dma_display->drawPixel(x, y, usPalette[*s++]); // color 565
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
} /* GIFDraw() */
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void * GIFOpenFile(const char *fname, int32_t *pSize)
|
||||
{
|
||||
Serial.print("Playing gif: ");
|
||||
Serial.println(fname);
|
||||
f = FILESYSTEM.open(fname);
|
||||
if (f)
|
||||
{
|
||||
*pSize = f.size();
|
||||
return (void *)&f;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
} /* GIFOpenFile() */
|
||||
|
||||
void GIFCloseFile(void *pHandle)
|
||||
{
|
||||
File *f = static_cast<File *>(pHandle);
|
||||
if (f != NULL)
|
||||
f->close();
|
||||
} /* GIFCloseFile() */
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t GIFReadFile(GIFFILE *pFile, uint8_t *pBuf, int32_t iLen)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int32_t iBytesRead;
|
||||
iBytesRead = iLen;
|
||||
File *f = static_cast<File *>(pFile->fHandle);
|
||||
// Note: If you read a file all the way to the last byte, seek() stops working
|
||||
if ((pFile->iSize - pFile->iPos) < iLen)
|
||||
iBytesRead = pFile->iSize - pFile->iPos - 1; // <-- ugly work-around
|
||||
if (iBytesRead <= 0)
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
iBytesRead = (int32_t)f->read(pBuf, iBytesRead);
|
||||
pFile->iPos = f->position();
|
||||
return iBytesRead;
|
||||
} /* GIFReadFile() */
|
||||
|
||||
int32_t GIFSeekFile(GIFFILE *pFile, int32_t iPosition)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i = micros();
|
||||
File *f = static_cast<File *>(pFile->fHandle);
|
||||
f->seek(iPosition);
|
||||
pFile->iPos = (int32_t)f->position();
|
||||
i = micros() - i;
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Seek time = %d us\n", i);
|
||||
return pFile->iPos;
|
||||
} /* GIFSeekFile() */
|
||||
|
||||
unsigned long start_tick = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
void ShowGIF(char *name)
|
||||
{
|
||||
start_tick = millis();
|
||||
|
||||
if (gif.open(name, GIFOpenFile, GIFCloseFile, GIFReadFile, GIFSeekFile, GIFDraw))
|
||||
{
|
||||
x_offset = (MATRIX_WIDTH - gif.getCanvasWidth())/2;
|
||||
if (x_offset < 0) x_offset = 0;
|
||||
y_offset = (MATRIX_HEIGHT - gif.getCanvasHeight())/2;
|
||||
if (y_offset < 0) y_offset = 0;
|
||||
Serial.printf("Successfully opened GIF; Canvas size = %d x %d\n", gif.getCanvasWidth(), gif.getCanvasHeight());
|
||||
Serial.flush();
|
||||
while (gif.playFrame(true, NULL))
|
||||
{
|
||||
if ( (millis() - start_tick) > 8000) { // we'll get bored after about 8 seconds of the same looping gif
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
gif.close();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} /* ShowGIF() */
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/************************* Arduino Sketch Setup and Loop() *******************************/
|
||||
void setup() {
|
||||
Serial.begin(115200);
|
||||
delay(1000);
|
||||
|
||||
HUB75_I2S_CFG mxconfig(
|
||||
PANEL_RES_X, // module width
|
||||
PANEL_RES_Y, // module height
|
||||
PANEL_CHAIN // Chain length
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
// mxconfig.gpio.e = 18;
|
||||
// mxconfig.clkphase = false;
|
||||
//mxconfig.driver = HUB75_I2S_CFG::FM6126A;
|
||||
|
||||
// Display Setup
|
||||
dma_display = new MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA(mxconfig);
|
||||
dma_display->begin();
|
||||
dma_display->setBrightness8(128); //0-255
|
||||
dma_display->clearScreen();
|
||||
dma_display->fillScreen(myWHITE);
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("Starting AnimatedGIFs Sketch");
|
||||
|
||||
// Start filesystem
|
||||
Serial.println(" * Loading SPIFFS");
|
||||
if(!SPIFFS.begin()){
|
||||
Serial.println("SPIFFS Mount Failed");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
dma_display->begin();
|
||||
|
||||
/* all other pixel drawing functions can only be called after .begin() */
|
||||
dma_display->fillScreen(dma_display->color565(0, 0, 0));
|
||||
gif.begin(LITTLE_ENDIAN_PIXELS);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
String gifDir = "/gifs"; // play all GIFs in this directory on the SD card
|
||||
char filePath[256] = { 0 };
|
||||
File root, gifFile;
|
||||
|
||||
void loop()
|
||||
{
|
||||
while (1) // run forever
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
root = FILESYSTEM.open(gifDir);
|
||||
if (root)
|
||||
{
|
||||
gifFile = root.openNextFile();
|
||||
while (gifFile)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (!gifFile.isDirectory()) // play it
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
// C-strings... urghh...
|
||||
memset(filePath, 0x0, sizeof(filePath));
|
||||
strcpy(filePath, gifFile.path());
|
||||
|
||||
// Show it.
|
||||
ShowGIF(filePath);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
gifFile.close();
|
||||
gifFile = root.openNextFile();
|
||||
}
|
||||
root.close();
|
||||
} // root
|
||||
|
||||
delay(1000); // pause before restarting
|
||||
|
||||
} // while
|
||||
}
|
||||
BIN
examples/AnimatedGIFPanel_SPIFFS/data/gifs/cartoon.gif
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 29 KiB |
BIN
examples/AnimatedGIFPanel_SPIFFS/data/gifs/ezgif.com-pacmn.gif
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 44 KiB |
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 39 KiB |
BIN
examples/AnimatedGIFPanel_SPIFFS/data/gifs/matrix-spin.gif
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 171 KiB |
BIN
examples/AnimatedGIFPanel_SPIFFS/data/gifs/parasite1.gif
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 58 KiB |
BIN
examples/AnimatedGIFPanel_SPIFFS/data/gifs/parasite2.gif
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 31 KiB |
BIN
examples/AnimatedGIFPanel_SPIFFS/data/gifs/shock-gs.gif
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 34 KiB |
|
|
@ -1,158 +1,67 @@
|
|||
/******************************************************************************
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
Steps to use
|
||||
-----------
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Steps to create a virtual display made up of a chain of panels in a grid
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
1) In the sketch (i.e. this example):
|
||||
Read the documentation!
|
||||
https://github.com/mrfaptastic/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-DMA/tree/master/examples/ChainedPanels
|
||||
|
||||
tl/dr:
|
||||
|
||||
- Set values for NUM_ROWS, NUM_COLS, PANEL_RES_X, PANEL_RES_Y, PANEL_CHAIN.
|
||||
There are comments beside them explaining what they are in more detail.
|
||||
- Set values for NUM_ROWS, NUM_COLS, PANEL_RES_X, PANEL_RES_Y, PANEL_CHAIN_TYPE.
|
||||
|
||||
- Other than where the matrix is defined and matrix.begin in the setup, you
|
||||
should now be using the virtual display for everything (drawing pixels, writing text etc).
|
||||
You can do a find and replace of all calls if it's an existing sketch
|
||||
(just make sure you don't replace the definition and the matrix.begin)
|
||||
|
||||
- If the sketch makes use of MATRIX_HEIGHT or MATRIX_WIDTH, these will need to be
|
||||
replaced with the width and height of your virtual screen.
|
||||
Either make new defines and use that, or you can use virtualDisp.width() or .height()
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks to:
|
||||
|
||||
* Brian Lough for the original example as raised in this issue:
|
||||
https://github.com/mrfaptastic/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA/issues/26
|
||||
|
||||
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/brianlough
|
||||
Tindie: https://www.tindie.com/stores/brianlough/
|
||||
Twitter: https://twitter.com/witnessmenow
|
||||
|
||||
* Galaxy-Man for the kind donation of panels make/test that this is possible:
|
||||
https://github.com/Galaxy-Man
|
||||
|
||||
*****************************************************************************/
|
||||
// 1) Include key virtual display library
|
||||
#include <ESP32-VirtualMatrixPanel-I2S-DMA.h>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/******************************************************************************
|
||||
* VIRTUAL DISPLAY / MATRIX PANEL CHAINING CONFIGURATION
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Note 1: If chaining from the top right to the left, and then S curving down
|
||||
* then serpentine_chain = true and top_down_chain = true
|
||||
* (these being the last two parameters of the virtualDisp(...) constructor.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Note 2: If chaining starts from the bottom up, then top_down_chain = false.
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Note 3: By default, this library has serpentine_chain = true, that is, every
|
||||
* second row has the panels 'upside down' (rotated 180), so the output
|
||||
* pin of the row above is right above the input connector of the next
|
||||
* row.
|
||||
|
||||
Example 1 panel chaining:
|
||||
+-----------------+-----------------+-------------------+
|
||||
| 64x32px PANEL 3 | 64x32px PANEL 2 | 64x32px PANEL 1 |
|
||||
| ------------ <-------- | ------------xx |
|
||||
| [OUT] | [IN] | [OUT] [IN] | [OUT] [ESP IN] |
|
||||
+--------|--------+-----------------+-------------------+
|
||||
| 64x32px|PANEL 4 | 64x32px PANEL 5 | 64x32px PANEL 6 |
|
||||
| \|/ ----------> | -----> |
|
||||
| [IN] [OUT] | [IN] [OUT] | [IN] [OUT] |
|
||||
+-----------------+-----------------+-------------------+
|
||||
|
||||
Example 1 configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
#define PANEL_RES_X 64 // Number of pixels wide of each INDIVIDUAL panel module.
|
||||
#define PANEL_RES_Y 32 // Number of pixels tall of each INDIVIDUAL panel module.
|
||||
|
||||
#define NUM_ROWS 2 // Number of rows of chained INDIVIDUAL PANELS
|
||||
#define NUM_COLS 3 // Number of INDIVIDUAL PANELS per ROW
|
||||
|
||||
virtualDisp(dma_display, NUM_ROWS, NUM_COLS, PANEL_RES_X, PANEL_RES_Y, true, true);
|
||||
|
||||
= 192x64 px virtual display, with the top left of panel 3 being pixel co-ord (0,0)
|
||||
|
||||
==========================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Example 2 panel chaining:
|
||||
|
||||
+-------------------+
|
||||
| 64x32px PANEL 1 |
|
||||
| ----------------- |
|
||||
| [OUT] [ESP IN] |
|
||||
+-------------------+
|
||||
| 64x32px PANEL 2 |
|
||||
| |
|
||||
| [IN] [OUT] |
|
||||
+-------------------+
|
||||
| 64x32px PANEL 3 |
|
||||
| |
|
||||
| [OUT] [IN] |
|
||||
+-------------------+
|
||||
| 64x32px PANEL 4 |
|
||||
| |
|
||||
| [IN] [OUT] |
|
||||
+-------------------+
|
||||
|
||||
Example 2 configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
#define PANEL_RES_X 64 // Number of pixels wide of each INDIVIDUAL panel module.
|
||||
#define PANEL_RES_Y 32 // Number of pixels tall of each INDIVIDUAL panel module.
|
||||
|
||||
#define NUM_ROWS 4 // Number of rows of chained INDIVIDUAL PANELS
|
||||
#define NUM_COLS 1 // Number of INDIVIDUAL PANELS per ROW
|
||||
|
||||
virtualDisp(dma_display, NUM_ROWS, NUM_COLS, PANEL_RES_X, PANEL_RES_Y, true, true);
|
||||
|
||||
virtualDisp(dma_display, NUM_ROWS, NUM_COLS, PANEL_RES_X, PANEL_RES_Y, true, true);
|
||||
|
||||
= 128x64 px virtual display, with the top left of panel 1 being pixel co-ord (0,0)
|
||||
|
||||
==========================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Example 3 panel chaining (bottom up):
|
||||
|
||||
+-----------------+-----------------+
|
||||
| 64x32px PANEL 4 | 64x32px PANEL 3 |
|
||||
| <---------- |
|
||||
| [OUT] [IN] | [OUT] [in] |
|
||||
+-----------------+-----------------+
|
||||
| 64x32px PANEL 1 | 64x32px PANEL 2 |
|
||||
| ----------> |
|
||||
| [ESP IN] [OUT] | [IN] [OUT] |
|
||||
+-----------------+-----------------+
|
||||
|
||||
Example 1 configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
// 2) Set configuration
|
||||
#define PANEL_RES_X 64 // Number of pixels wide of each INDIVIDUAL panel module.
|
||||
#define PANEL_RES_Y 32 // Number of pixels tall of each INDIVIDUAL panel module.
|
||||
|
||||
#define NUM_ROWS 2 // Number of rows of chained INDIVIDUAL PANELS
|
||||
#define NUM_COLS 2 // Number of INDIVIDUAL PANELS per ROW
|
||||
#define PANEL_CHAIN NUM_ROWS*NUM_COLS // total number of panels chained one to another
|
||||
|
||||
virtualDisp(dma_display, NUM_ROWS, NUM_COLS, PANEL_RES_X, PANEL_RES_Y, true, false);
|
||||
/* Configure the serpetine chaining approach. Options are:
|
||||
CHAIN_TOP_LEFT_DOWN
|
||||
CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN
|
||||
CHAIN_BOTTOM_LEFT_UP
|
||||
CHAIN_BOTTOM_RIGHT_UP
|
||||
|
||||
= 128x64 px virtual display, with the top left of panel 4 being pixel co-ord (0,0)
|
||||
The location (i.e. 'TOP_LEFT', 'BOTTOM_RIGHT') etc. refers to the starting point where
|
||||
the ESP32 is located, and how the chain of panels will 'roll out' from there.
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
In this example we're using 'CHAIN_BOTTOM_LEFT_UP' which would look like this in the real world:
|
||||
|
||||
Chain of 4 x 64x32 panels with the ESP at the BOTTOM_LEFT:
|
||||
|
||||
+---------+---------+
|
||||
| 4 | 3 |
|
||||
| | |
|
||||
+---------+---------+
|
||||
| 1 | 2 |
|
||||
| (ESP) | |
|
||||
+---------+---------+
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
#define VIRTUAL_MATRIX_CHAIN_TYPE CHAIN_BOTTOM_LEFT_UP
|
||||
|
||||
#define PANEL_RES_X 64 // Number of pixels wide of each INDIVIDUAL panel module.
|
||||
#define PANEL_RES_Y 32 // Number of pixels tall of each INDIVIDUAL panel module.
|
||||
// 3) Create the runtime objects to use
|
||||
|
||||
#define NUM_ROWS 2 // Number of rows of chained INDIVIDUAL PANELS
|
||||
#define NUM_COLS 2 // Number of INDIVIDUAL PANELS per ROW
|
||||
#define PANEL_CHAIN NUM_ROWS*NUM_COLS // total number of panels chained one to another
|
||||
// placeholder for the matrix object
|
||||
MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA *dma_display = nullptr;
|
||||
|
||||
// Change this to your needs, for details on VirtualPanel pls read the PDF!
|
||||
#define SERPENT true
|
||||
#define TOPDOWN false
|
||||
|
||||
// library includes
|
||||
#include <ESP32-VirtualMatrixPanel-I2S-DMA.h>
|
||||
|
||||
// placeholder for the matrix object
|
||||
MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA *dma_display = nullptr;
|
||||
|
||||
// placeholder for the virtual display object
|
||||
VirtualMatrixPanel *virtualDisp = nullptr;
|
||||
// placeholder for the virtual display object
|
||||
VirtualMatrixPanel *virtualDisp = nullptr;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/******************************************************************************
|
||||
|
|
@ -203,37 +112,58 @@ void setup() {
|
|||
Serial.println("****** !KABOOM! I2S memory allocation failed ***********");
|
||||
|
||||
// create VirtualDisplay object based on our newly created dma_display object
|
||||
virtualDisp = new VirtualMatrixPanel((*dma_display), NUM_ROWS, NUM_COLS, PANEL_RES_X, PANEL_RES_Y, SERPENT, TOPDOWN);
|
||||
virtualDisp = new VirtualMatrixPanel((*dma_display), NUM_ROWS, NUM_COLS, PANEL_RES_X, PANEL_RES_Y, VIRTUAL_MATRIX_CHAIN_TYPE);
|
||||
|
||||
// So far so good, so continue
|
||||
virtualDisp->fillScreen(virtualDisp->color444(0, 0, 0));
|
||||
virtualDisp->drawDisplayTest(); // draw text numbering on each screen to check connectivity
|
||||
|
||||
delay(3000);
|
||||
// delay(1000);
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("Chain of 64x32 panels for this example:");
|
||||
Serial.println("+--------+---------+");
|
||||
Serial.println("| 4 | 3 |");
|
||||
Serial.println("| | |");
|
||||
Serial.println("+--------+---------+");
|
||||
Serial.println("| 1 | 2 |");
|
||||
Serial.println("| (ESP) | |");
|
||||
Serial.println("+--------+---------+");
|
||||
Serial.println("Chain of 4x 64x32 panels for this example:");
|
||||
Serial.println("+---------+---------+");
|
||||
Serial.println("| 4 | 3 |");
|
||||
Serial.println("| | |");
|
||||
Serial.println("+---------+---------+");
|
||||
Serial.println("| 1 | 2 |");
|
||||
Serial.println("| (ESP32) | |");
|
||||
Serial.println("+---------+---------+");
|
||||
|
||||
// draw blue text
|
||||
virtualDisp->setFont(&FreeSansBold12pt7b);
|
||||
virtualDisp->setTextColor(virtualDisp->color565(0, 0, 255));
|
||||
virtualDisp->setTextSize(2);
|
||||
virtualDisp->setCursor(10, virtualDisp->height()-20);
|
||||
|
||||
virtualDisp->setTextSize(3);
|
||||
virtualDisp->setCursor(0, virtualDisp->height()- ((virtualDisp->height()-45)/2));
|
||||
virtualDisp->print("ABCD");
|
||||
|
||||
// Red text inside red rect (2 pix in from edge)
|
||||
virtualDisp->print("1234");
|
||||
virtualDisp->drawRect(1,1, virtualDisp->width()-2, virtualDisp->height()-2, virtualDisp->color565(255,0,0));
|
||||
|
||||
// White line from top left to bottom right
|
||||
virtualDisp->drawLine(0,0, virtualDisp->width()-1, virtualDisp->height()-1, virtualDisp->color565(255,255,255));
|
||||
|
||||
virtualDisp->drawDisplayTest(); // re draw text numbering on each screen to check connectivity
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void loop() {
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
} // end loop
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/*****************************************************************************
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks to:
|
||||
|
||||
* Brian Lough for the original example as raised in this issue:
|
||||
https://github.com/mrfaptastic/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA/issues/26
|
||||
|
||||
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/brianlough
|
||||
Tindie: https://www.tindie.com/stores/brianlough/
|
||||
Twitter: https://twitter.com/witnessmenow
|
||||
|
||||
* Galaxy-Man for the kind donation of panels make/test that this is possible:
|
||||
https://github.com/Galaxy-Man
|
||||
|
||||
*****************************************************************************/
|
||||
|
|
@ -2,6 +2,8 @@
|
|||
|
||||
This is the PatternPlasma Demo adopted for use with multiple LED Matrix Panel displays arranged in a non standard order (i.e. a grid) to make a bigger display.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### What do we mean by 'non standard order'? ###
|
||||
|
||||
When you link / chain multiple panels together, the ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA library treats as one wide horizontal panel. This would be a 'standard' (default) order.
|
||||
|
|
@ -10,12 +12,12 @@ Non-standard order is essentially the creation of a non-horizontal-only display
|
|||
|
||||
For example: You bought four (4) 64x32px panels, and wanted to use them to create a 128x64pixel display. You would use the VirtualMatrixPanel class.
|
||||
|
||||
[Refer to this document](VirtualMatrixPanel.pdf) for an explanation and refer to this example on how to use.
|
||||
[Refer to this document](https://github.com/mrfaptastic/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-DMA/blob/master/doc/VirtualMatrixPanel.pdf) for an explanation and refer to this example on how to use.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Steps to Use ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Refer to this document](VirtualMatrixPanel.pdf) for an explanation and refer to this example on how to use.
|
||||
1. [Refer to this document](https://github.com/mrfaptastic/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-DMA/blob/master/doc/VirtualMatrixPanel.pdf) for an explanation and refer to this example on how to use.
|
||||
|
||||
2. In your Arduino sketch, configure these defines accordingly:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -24,7 +26,15 @@ For example: You bought four (4) 64x32px panels, and wanted to use them to creat
|
|||
|
||||
#define NUM_ROWS 2 // Number of rows of chained INDIVIDUAL PANELS
|
||||
#define NUM_COLS 2 // Number of INDIVIDUAL PANELS per ROW
|
||||
|
||||
#define PANEL_CHAIN NUM_ROWS*NUM_COLS // total number of panels chained one to another
|
||||
|
||||
#define VIRTUAL_MATRIX_CHAIN_TYPE <INSERT CHAINING TYPE HERE - Refer to documentation or example>
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
VIRTUAL_MATRIX_CHAIN_TYPE's:
|
||||
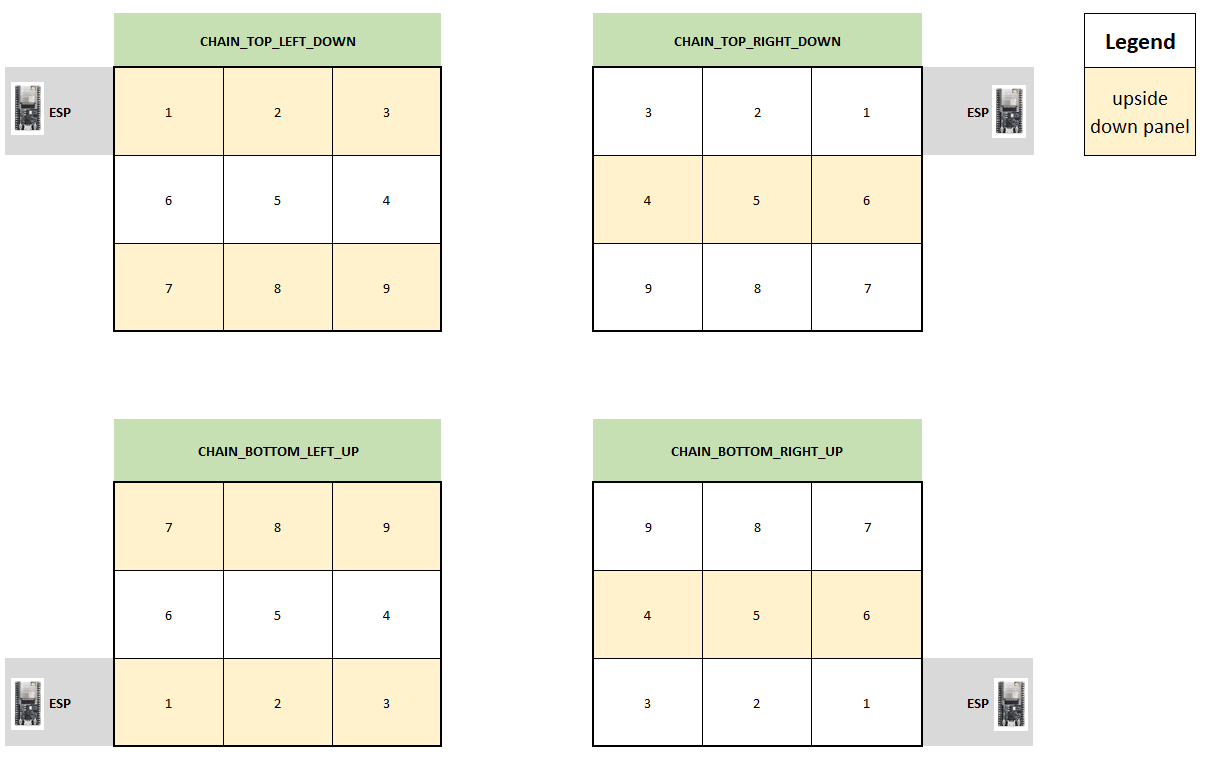
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
3. In your Arduino sketch, use the 'VirtualMatrixPanel' class instance (virtualDisp) to draw to the display (i.e. drawPixel), instead of the underling MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA class instance (dma_display).
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -117,7 +117,7 @@ void setup()
|
|||
matrix->setBrightness8(96); // range is 0-255, 0 - 0%, 255 - 100%
|
||||
|
||||
// create VirtualDisplay object based on our newly created dma_display object
|
||||
virtualDisp = new VirtualMatrixPanel((*matrix), NUM_ROWS, NUM_COLS, PANEL_RES_X, PANEL_RES_Y, SERPENT, TOPDOWN);
|
||||
virtualDisp = new VirtualMatrixPanel((*matrix), NUM_ROWS, NUM_COLS, PANEL_RES_X, PANEL_RES_Y, CHAIN_TOP_LEFT_DOWN);
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.println("**************** Starting Aurora Effects Demo ****************");
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -91,7 +91,7 @@
|
|||
delay(500);
|
||||
|
||||
// create FourScanPanellay object based on our newly created dma_display object
|
||||
FourScanPanel = new VirtualMatrixPanel((*dma_display), NUM_ROWS, NUM_COLS, PANEL_RES_X, PANEL_RES_Y, SERPENT, TOPDOWN);
|
||||
FourScanPanel = new VirtualMatrixPanel((*dma_display), NUM_ROWS, NUM_COLS, PANEL_RES_X, PANEL_RES_Y);
|
||||
|
||||
// THE IMPORTANT BIT BELOW!
|
||||
FourScanPanel->setPhysicalPanelScanRate(FOUR_SCAN_32PX_HIGH);
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -7,6 +7,10 @@
|
|||
MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA *dma_display = nullptr;
|
||||
|
||||
void setup() {
|
||||
|
||||
Serial.begin(112500);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
HUB75_I2S_CFG::i2s_pins _pins={
|
||||
25, //R1_PIN,
|
||||
26, //G1_PIN,
|
||||
|
|
@ -26,8 +30,8 @@ void setup() {
|
|||
HUB75_I2S_CFG mxconfig(
|
||||
PANEL_RES_X, // Module width
|
||||
PANEL_RES_Y, // Module height
|
||||
PANEL_CHAIN, // chain length
|
||||
_pins // pin mapping
|
||||
PANEL_CHAIN //, // chain length
|
||||
//_pins // pin mapping -- uncomment if providing own custom pin mapping as per above.
|
||||
);
|
||||
//mxconfig.clkphase = false;
|
||||
//mxconfig.driver = HUB75_I2S_CFG::FM6126A;
|
||||
|
|
@ -40,12 +44,13 @@ void setup() {
|
|||
|
||||
void loop() {
|
||||
// Canvas loop
|
||||
float t = (float)(millis()%4000)/4000.f;
|
||||
float tt = (float)((millis()%16000)/16000.f;
|
||||
float t = (float) ((millis()%4000)/4000.f);
|
||||
float tt = (float) ((millis()%16000)/16000.f);
|
||||
|
||||
for(int x = 0; x < PANEL_RES_X*PANEL_CHAIN; x++){
|
||||
for(int x = 0; x < (PANEL_RES_X*PANEL_CHAIN); x++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
// calculate the overal shade
|
||||
float f = ((sin(tt-(float)x/PANEL_RES_Y/32.)*2.f*PI)+1)/2)*255;
|
||||
float f = (((sin(tt-(float)x/PANEL_RES_Y/32.)*2.f*PI)+1)/2)*255;
|
||||
// calculate hue spectrum into rgb
|
||||
float r = max(min(cosf(2.f*PI*(t+((float)x/PANEL_RES_Y+0.f)/3.f))+0.5f,1.f),0.f);
|
||||
float g = max(min(cosf(2.f*PI*(t+((float)x/PANEL_RES_Y+1.f)/3.f))+0.5f,1.f),0.f);
|
||||
|
|
@ -116,7 +116,7 @@ void setup(){
|
|||
chain->begin();
|
||||
chain->setBrightness8(255);
|
||||
// create VirtualDisplay object based on our newly created dma_display object
|
||||
matrix = new VirtualMatrixPanel((*chain), NUM_ROWS, NUM_COLS, PANEL_WIDTH, PANEL_HEIGHT, SERPENT, TOPDOWN);
|
||||
matrix = new VirtualMatrixPanel((*chain), NUM_ROWS, NUM_COLS, PANEL_WIDTH, PANEL_HEIGHT, CHAIN_TOP_LEFT_DOWN);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
ledbuff = (CRGB *)malloc(NUM_LEDS * sizeof(CRGB)); // allocate buffer for some tests
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
12
examples/esp-idf/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
|||
# ESP-IDF default build directory
|
||||
build
|
||||
|
||||
# Temporary files
|
||||
*.swp
|
||||
|
||||
# lock files for examples and components
|
||||
dependencies.lock
|
||||
|
||||
sdkconfig*
|
||||
# Unignore sdkconfig.defaults
|
||||
!sdkconfig.defaults
|
||||
10
examples/esp-idf/with-gfx/CMakeLists.txt
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
|||
# This is a boilerplate top-level project CMakeLists.txt file.
|
||||
# This is the primary file which CMake uses to learn how to build the project.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Most of the important stuff happens in the 'main' directory.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# See https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/esp32/api-guides/build-system.html#example-project for more details.
|
||||
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5)
|
||||
|
||||
include($ENV{IDF_PATH}/tools/cmake/project.cmake)
|
||||
project(with-gfx)
|
||||
17
examples/esp-idf/with-gfx/README.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
|||
# ESP-IDF Example With Adafruit GFX Library
|
||||
|
||||
This folder contains example code for using this library with `esp-idf` and the [Adafruit GFX library](https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit-GFX-Library).
|
||||
|
||||
First, follow the [Getting Started Guide for ESP-IDF](https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/esp32/get-started/index.html) to install ESP-IDF onto your computer.
|
||||
|
||||
When you are ready to start your first project with this library, follow folow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Copy the files in this folder (and sub folders) into a new directory for your project.
|
||||
1. Clone the required repositories:
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/mrfaptastic/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-DMA.git components/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit-GFX-Library.git components/Adafruit-GFX-Library
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/adafruit/Adafruit_BusIO.git components/Adafruit_BusIO
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/espressif/arduino-esp32.git components/arduino
|
||||
```
|
||||
1. Build your project: `idf.py build`
|
||||
4
examples/esp-idf/with-gfx/components/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
|||
# Ignore everything in this directory
|
||||
*
|
||||
# Except this file
|
||||
!.gitignore
|
||||
5
examples/esp-idf/with-gfx/main/CMakeLists.txt
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
|||
idf_component_register(
|
||||
SRC_DIRS "." ${SRCDIRS}
|
||||
INCLUDE_DIRS ${INCLUDEDIRS}
|
||||
REQUIRES ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA
|
||||
)
|
||||
14
examples/esp-idf/with-gfx/main/main.cpp
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
|||
#include "ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA.h"
|
||||
|
||||
MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA *dma_display = nullptr;
|
||||
|
||||
extern "C" void app_main() {
|
||||
HUB75_I2S_CFG mxconfig(/* width = */ 64, /* height = */ 64, /* chain = */ 1);
|
||||
|
||||
dma_display = new MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA(mxconfig);
|
||||
dma_display->begin();
|
||||
dma_display->setBrightness8(80);
|
||||
dma_display->clearScreen();
|
||||
// `println` is only available when the Adafruit GFX library is used.
|
||||
dma_display->println("Test message");
|
||||
}
|
||||
1
examples/esp-idf/with-gfx/sdkconfig.defaults
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
|||
CONFIG_FREERTOS_HZ=1000
|
||||
10
examples/esp-idf/without-gfx/CMakeLists.txt
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
|||
# This is a boilerplate top-level project CMakeLists.txt file.
|
||||
# This is the primary file which CMake uses to learn how to build the project.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Most of the important stuff happens in the 'main' directory.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# See https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/esp32/api-guides/build-system.html#example-project for more details.
|
||||
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5)
|
||||
|
||||
include($ENV{IDF_PATH}/tools/cmake/project.cmake)
|
||||
project(without-gfx)
|
||||
14
examples/esp-idf/without-gfx/README.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
|||
# ESP-IDF Example Without Adafruit GFX Library
|
||||
|
||||
This folder contains example code for using this library with `esp-idf`.
|
||||
|
||||
First, follow the [Getting Started Guide for ESP-IDF](https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/esp32/get-started/index.html) to install ESP-IDF onto your computer.
|
||||
|
||||
When you are ready to start your first project with this library, follow folow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Copy the files in this folder (and sub folders) into a new directory for your project.
|
||||
1. Clone the required repositories:
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/mrfaptastic/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-DMA.git components/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA
|
||||
```
|
||||
1. Build your project: `idf.py build`
|
||||
4
examples/esp-idf/without-gfx/components/.gitignore
vendored
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
|||
# Ignore everything in this directory
|
||||
*
|
||||
# Except this file
|
||||
!.gitignore
|
||||
5
examples/esp-idf/without-gfx/main/CMakeLists.txt
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
|||
idf_component_register(
|
||||
SRC_DIRS "." ${SRCDIRS}
|
||||
INCLUDE_DIRS ${INCLUDEDIRS}
|
||||
REQUIRES ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA
|
||||
)
|
||||
12
examples/esp-idf/without-gfx/main/main.cpp
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
|||
#include "ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-I2S-DMA.h"
|
||||
|
||||
MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA *dma_display = nullptr;
|
||||
|
||||
extern "C" void app_main() {
|
||||
HUB75_I2S_CFG mxconfig(/* width = */ 64, /* height = */ 64, /* chain = */ 1);
|
||||
|
||||
dma_display = new MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA(mxconfig);
|
||||
dma_display->begin();
|
||||
dma_display->setBrightness8(80);
|
||||
dma_display->clearScreen();
|
||||
}
|
||||
1
examples/esp-idf/without-gfx/sdkconfig.defaults
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
|||
CONFIG_ESP32_HUB75_USE_GFX=n
|
||||
|
|
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
"name": "ESP32 HUB75 LED MATRIX PANEL DMA Display",
|
||||
"version": "3.0.5",
|
||||
"version": "3.0.9",
|
||||
"description": "An Adafruit GFX compatible library for LED matrix modules which uses DMA for ultra-fast refresh rates and therefore very low CPU usage.",
|
||||
"keywords": "hub75, esp32, esp32s2, esp32s3, display, dma, rgb matrix",
|
||||
"repository": {
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
|||
name=ESP32 HUB75 LED MATRIX PANEL DMA Display
|
||||
version= 3.0.5
|
||||
version= 3.0.9
|
||||
author=Faptastic
|
||||
maintainer=Faptastic
|
||||
sentence=HUB75 LED Matrix Library for ESP32, ESP32-S2 and ESP32-S3
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -27,6 +27,9 @@ void MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA::shiftDriver(const HUB75_I2S_CFG& _cfg){
|
|||
case HUB75_I2S_CFG::FM6126A:
|
||||
fm6124init(_cfg);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case HUB75_I2S_CFG::DP3246_SM5368:
|
||||
dp3246init(_cfg);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case HUB75_I2S_CFG::MBI5124:
|
||||
/* MBI5124 chips must be clocked with positive-edge, since it's LAT signal
|
||||
* resets on clock's rising edge while high
|
||||
|
|
@ -49,6 +52,7 @@ void MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA::fm6124init(const HUB75_I2S_CFG& _cfg) {
|
|||
bool REG2[16] = {0,0,0,0,0, 0,0,0,0,1,0, 0,0,0,0,0}; // a single bit enables the matrix output
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint8_t _pin:{_cfg.gpio.r1, _cfg.gpio.r2, _cfg.gpio.g1, _cfg.gpio.g2, _cfg.gpio.b1, _cfg.gpio.b2, _cfg.gpio.clk, _cfg.gpio.lat, _cfg.gpio.oe}){
|
||||
gpio_reset_pin((gpio_num_t)_pin); // some pins are not in gpio mode after reset => https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/esp32/api-reference/peripherals/gpio.html#gpio-summary
|
||||
gpio_set_direction((gpio_num_t) _pin, GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT);
|
||||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t) _pin, LOW);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -97,4 +101,90 @@ void MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA::fm6124init(const HUB75_I2S_CFG& _cfg) {
|
|||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t) _cfg.gpio.lat, LOW);
|
||||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t) _cfg.gpio.oe, LOW); // Enable Display
|
||||
CLK_PULSE
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA::dp3246init(const HUB75_I2S_CFG& _cfg) {
|
||||
|
||||
ESP_LOGI("LEDdrivers", "MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA - initializing DP3246 driver...");
|
||||
|
||||
// DP3246 needs positive clock edge
|
||||
m_cfg.clkphase = true;
|
||||
|
||||
// 15:13 3 000 reserved
|
||||
// 12:9 4 0000 OE widening (= OE_ADD * 6ns)
|
||||
// 8 1 0 reserved
|
||||
// 7:0 8 11111111 Iout = (Igain+1)/256 * 17.6 / Rext
|
||||
bool REG1[16] = { 0,0,0, 0,0,0,0, 0, 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1 }; // MSB first
|
||||
|
||||
// 15:11 5 11111 Blanking potential selection, step 77mV, 00000: VDD-0.8V
|
||||
// 10:8 3 111 Constant current source output inflection point selection
|
||||
// 7 1 0 Disable dead pixel removel, 1: Enable
|
||||
// 6 1 0 0->1: (OPEN_DET rising edge) start detection, 0: reset to ready-to-detect state
|
||||
// 5 1 0 0: Enable black screen power saving, 1: Turn off the black screen to save energy
|
||||
// 4 1 0 0: Do not enable the fading function, 1: Enable the fade function
|
||||
// 3 1 0 Reserved
|
||||
// 2:0 3 000 000: single edge pass, others: double edge transfer
|
||||
bool REG2[16] = { 1,1,1,1,1, 1,1,1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,0,0 }; // MSB first
|
||||
|
||||
for (uint8_t _pin : {_cfg.gpio.r1, _cfg.gpio.r2, _cfg.gpio.g1, _cfg.gpio.g2, _cfg.gpio.b1, _cfg.gpio.b2, _cfg.gpio.clk, _cfg.gpio.lat, _cfg.gpio.oe}) {
|
||||
gpio_reset_pin((gpio_num_t)_pin); // some pins are not in gpio mode after reset => https://docs.espressif.com/projects/esp-idf/en/latest/esp32/api-reference/peripherals/gpio.html#gpio-summary
|
||||
gpio_set_direction((gpio_num_t)_pin, GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT);
|
||||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t)_pin, LOW);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t)_cfg.gpio.oe, HIGH); // disable Display
|
||||
|
||||
// clear registers - this seems to help with reliability
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < PIXELS_PER_ROW; ++l) {
|
||||
if (l == PIXELS_PER_ROW - 3) { // DP3246 wants the latch dropped for 3 clk cycles
|
||||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t)_cfg.gpio.lat, HIGH);
|
||||
}
|
||||
CLK_PULSE
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t)_cfg.gpio.lat, LOW);
|
||||
|
||||
// Send Data to control register REG1
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < PIXELS_PER_ROW; l++) {
|
||||
for (uint8_t _pin : {_cfg.gpio.r1, _cfg.gpio.r2, _cfg.gpio.g1, _cfg.gpio.g2, _cfg.gpio.b1, _cfg.gpio.b2})
|
||||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t)_pin, REG1[l % 16]); // we have 16 bits shifters and write the same value all over the matrix array
|
||||
|
||||
if (l == PIXELS_PER_ROW - 11) { // pull the latch 11 clocks before the end of matrix so that REG1 starts counting to save the value
|
||||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t)_cfg.gpio.lat, HIGH);
|
||||
}
|
||||
CLK_PULSE
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// drop the latch and save data to the REG1 all over the DP3246 chips
|
||||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t)_cfg.gpio.lat, LOW);
|
||||
|
||||
// Send Data to control register REG2
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < PIXELS_PER_ROW; l++) {
|
||||
for (uint8_t _pin : {_cfg.gpio.r1, _cfg.gpio.r2, _cfg.gpio.g1, _cfg.gpio.g2, _cfg.gpio.b1, _cfg.gpio.b2})
|
||||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t)_pin, REG2[l % 16]); // we have 16 bits shifters and we write the same value all over the matrix array
|
||||
|
||||
if (l == PIXELS_PER_ROW - 12) { // pull the latch 12 clocks before the end of matrix so that REG2 starts counting to save the value
|
||||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t)_cfg.gpio.lat, HIGH);
|
||||
}
|
||||
CLK_PULSE
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// drop the latch and save data to the REG2 all over the DP3246 chips
|
||||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t)_cfg.gpio.lat, LOW);
|
||||
CLK_PULSE
|
||||
|
||||
// blank data regs to keep matrix clear after manipulations
|
||||
for (uint8_t _pin : {_cfg.gpio.r1, _cfg.gpio.r2, _cfg.gpio.g1, _cfg.gpio.g2, _cfg.gpio.b1, _cfg.gpio.b2})
|
||||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t)_pin, LOW);
|
||||
|
||||
for (int l = 0; l < PIXELS_PER_ROW; ++l) {
|
||||
if (l == PIXELS_PER_ROW - 3) { // DP3246 wants the latch dropped for 3 clk cycles
|
||||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t)_cfg.gpio.lat, HIGH);
|
||||
}
|
||||
CLK_PULSE
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t)_cfg.gpio.lat, LOW);
|
||||
gpio_set_level((gpio_num_t)_cfg.gpio.oe, LOW); // enable Display
|
||||
CLK_PULSE
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
@ -10,16 +10,16 @@
|
|||
|
||||
However, the function of this class has expanded now to also manage
|
||||
the output for
|
||||
|
||||
1) TWO scan panels = Two rows updated in parallel.
|
||||
* 64px high panel = sometimes referred to as 1/32 scan
|
||||
* 32px high panel = sometimes referred to as 1/16 scan
|
||||
* 16px high panel = sometimes referred to as 1/8 scan
|
||||
|
||||
2) FOUR scan panels = Four rows updated in parallel
|
||||
* 32px high panel = sometimes referred to as 1/8 scan
|
||||
* 16px high panel = sometimes referred to as 1/4 scan
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1) TWO scan panels = Two rows updated in parallel.
|
||||
* 64px high panel = sometimes referred to as 1/32 scan
|
||||
* 32px high panel = sometimes referred to as 1/16 scan
|
||||
* 16px high panel = sometimes referred to as 1/8 scan
|
||||
|
||||
2) FOUR scan panels = Four rows updated in parallel
|
||||
* 32px high panel = sometimes referred to as 1/8 scan
|
||||
* 16px high panel = sometimes referred to as 1/4 scan
|
||||
|
||||
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/brianlough
|
||||
Tindie: https://www.tindie.com/stores/brianlough/
|
||||
Twitter: https://twitter.com/witnessmenow
|
||||
|
|
@ -30,23 +30,41 @@
|
|||
#include <Fonts/FreeSansBold12pt7b.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// #include <iostream>
|
||||
|
||||
struct VirtualCoords
|
||||
{
|
||||
int16_t x;
|
||||
int16_t y;
|
||||
int16_t virt_row; // chain of panels row
|
||||
int16_t virt_col; // chain of panels col
|
||||
int16_t x;
|
||||
int16_t y;
|
||||
int16_t virt_row; // chain of panels row
|
||||
int16_t virt_col; // chain of panels col
|
||||
|
||||
VirtualCoords() : x(0), y(0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
}
|
||||
VirtualCoords() : x(0), y(0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
enum PANEL_SCAN_RATE
|
||||
{
|
||||
NORMAL_TWO_SCAN, NORMAL_ONE_SIXTEEN, // treated as the same
|
||||
FOUR_SCAN_32PX_HIGH,
|
||||
FOUR_SCAN_16PX_HIGH
|
||||
NORMAL_TWO_SCAN,
|
||||
NORMAL_ONE_SIXTEEN, // treated as the same
|
||||
FOUR_SCAN_32PX_HIGH,
|
||||
FOUR_SCAN_16PX_HIGH,
|
||||
FOUR_SCAN_64PX_HIGH
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Chaining approach... From the perspective of the DISPLAY / LED side of the chain of panels.
|
||||
enum PANEL_CHAIN_TYPE
|
||||
{
|
||||
CHAIN_NONE,
|
||||
CHAIN_TOP_LEFT_DOWN,
|
||||
CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN,
|
||||
CHAIN_BOTTOM_LEFT_UP,
|
||||
CHAIN_BOTTOM_RIGHT_UP,
|
||||
CHAIN_TOP_LEFT_DOWN_ZZ, /// ZigZag chaining. Might need a big ass cable to do this, all panels right way up.
|
||||
CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN_ZZ,
|
||||
CHAIN_BOTTOM_RIGHT_UP_ZZ,
|
||||
CHAIN_BOTTOM_LEFT_UP_ZZ
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef USE_GFX_ROOT
|
||||
|
|
@ -59,85 +77,92 @@ class VirtualMatrixPanel
|
|||
{
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
int16_t virtualResX;
|
||||
int16_t virtualResY;
|
||||
|
||||
int16_t vmodule_rows;
|
||||
int16_t vmodule_cols;
|
||||
|
||||
int16_t panelResX;
|
||||
int16_t panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
int16_t dmaResX; // The width of the chain in pixels (as the DMA engine sees it)
|
||||
|
||||
MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA *display;
|
||||
|
||||
VirtualMatrixPanel(MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA &disp, int _vmodule_rows, int _vmodule_cols, int _panelResX, int _panelResY, bool serpentine_chain = true, bool top_down_chain = false)
|
||||
VirtualMatrixPanel(MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA &disp, int _vmodule_rows, int _vmodule_cols, int _panelResX, int _panelResY, PANEL_CHAIN_TYPE _panel_chain_type = CHAIN_NONE)
|
||||
#ifdef USE_GFX_ROOT
|
||||
: GFX(_vmodule_cols * _panelResX, _vmodule_rows * _panelResY)
|
||||
: GFX(_vmodule_cols * _panelResX, _vmodule_rows * _panelResY)
|
||||
#elif !defined NO_GFX
|
||||
: Adafruit_GFX(_vmodule_cols * _panelResX, _vmodule_rows * _panelResY)
|
||||
: Adafruit_GFX(_vmodule_cols * _panelResX, _vmodule_rows * _panelResY)
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
{
|
||||
this->display = &disp;
|
||||
{
|
||||
this->display = &disp;
|
||||
|
||||
panelResX = _panelResX;
|
||||
panelResY = _panelResY;
|
||||
panel_chain_type = _panel_chain_type;
|
||||
|
||||
vmodule_rows = _vmodule_rows;
|
||||
vmodule_cols = _vmodule_cols;
|
||||
panelResX = _panelResX;
|
||||
panelResY = _panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
virtualResX = vmodule_cols * _panelResX;
|
||||
virtualResY = vmodule_rows * _panelResY;
|
||||
vmodule_rows = _vmodule_rows;
|
||||
vmodule_cols = _vmodule_cols;
|
||||
|
||||
dmaResX = panelResX * vmodule_rows * vmodule_cols;
|
||||
virtualResX = vmodule_cols * _panelResX;
|
||||
virtualResY = vmodule_rows * _panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Virtual Display width() and height() will return a real-world value. For example:
|
||||
* Virtual Display width: 128
|
||||
* Virtual Display height: 64
|
||||
*
|
||||
* So, not values that at 0 to X-1
|
||||
*/
|
||||
dmaResX = panelResX * vmodule_rows * vmodule_cols - 1;
|
||||
|
||||
_s_chain_party = serpentine_chain; // serpentine, or 'S' chain?
|
||||
_chain_top_down = top_down_chain;
|
||||
/* Virtual Display width() and height() will return a real-world value. For example:
|
||||
* Virtual Display width: 128
|
||||
* Virtual Display height: 64
|
||||
*
|
||||
* So, not values that at 0 to X-1
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
coords.x = coords.y = -1; // By default use an invalid co-ordinates that will be rejected by updateMatrixDMABuffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
coords.x = coords.y = -1; // By default use an invalid co-ordinates that will be rejected by updateMatrixDMABuffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// equivalent methods of the matrix library so it can be just swapped out.
|
||||
virtual void drawPixel(int16_t x, int16_t y, uint16_t color);
|
||||
virtual void fillScreen(uint16_t color); // overwrite adafruit implementation
|
||||
virtual void fillScreenRGB888(uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b);
|
||||
|
||||
void clearScreen() { display->clearScreen(); }
|
||||
void drawPixelRGB888(int16_t x, int16_t y, uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b);
|
||||
// equivalent methods of the matrix library so it can be just swapped out.
|
||||
void drawPixel(int16_t x, int16_t y, uint16_t color); // overwrite adafruit implementation
|
||||
void fillScreen(uint16_t color); // overwrite adafruit implementation
|
||||
void setRotation(int rotate); // overwrite adafruit implementation
|
||||
|
||||
void fillScreenRGB888(uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b);
|
||||
void clearScreen() { display->clearScreen(); }
|
||||
void drawPixelRGB888(int16_t x, int16_t y, uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b);
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef USE_GFX_ROOT
|
||||
// 24bpp FASTLED CRGB colour struct support
|
||||
void fillScreen(CRGB color);
|
||||
void drawPixel(int16_t x, int16_t y, CRGB color);
|
||||
// 24bpp FASTLED CRGB colour struct support
|
||||
void fillScreen(CRGB color);
|
||||
void drawPixel(int16_t x, int16_t y, CRGB color);
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
uint16_t color444(uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b) { return display->color444(r, g, b); }
|
||||
uint16_t color565(uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b) { return display->color565(r, g, b); }
|
||||
uint16_t color333(uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b) { return display->color333(r, g, b); }
|
||||
uint16_t color444(uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b)
|
||||
{
|
||||
return display->color444(r, g, b);
|
||||
}
|
||||
uint16_t color565(uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b) { return display->color565(r, g, b); }
|
||||
uint16_t color333(uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b) { return display->color333(r, g, b); }
|
||||
|
||||
void flipDMABuffer() { display->flipDMABuffer(); }
|
||||
void drawDisplayTest();
|
||||
void setRotate(bool rotate);
|
||||
void flipDMABuffer() { display->flipDMABuffer(); }
|
||||
void drawDisplayTest();
|
||||
|
||||
void setPhysicalPanelScanRate(PANEL_SCAN_RATE rate);
|
||||
void setPhysicalPanelScanRate(PANEL_SCAN_RATE rate);
|
||||
void setZoomFactor(int scale);
|
||||
|
||||
protected:
|
||||
virtual VirtualCoords getCoords(int16_t &x, int16_t &y);
|
||||
VirtualCoords coords;
|
||||
private:
|
||||
MatrixPanel_I2S_DMA *display;
|
||||
|
||||
bool _s_chain_party = true; // Are we chained? Ain't no party like a...
|
||||
bool _chain_top_down = false; // is the ESP at the top or bottom of the matrix of devices?
|
||||
bool _rotate = false;
|
||||
PANEL_CHAIN_TYPE panel_chain_type;
|
||||
PANEL_SCAN_RATE panel_scan_rate = NORMAL_TWO_SCAN;
|
||||
|
||||
PANEL_SCAN_RATE _panelScanRate = NORMAL_TWO_SCAN;
|
||||
virtual VirtualCoords getCoords(int16_t x, int16_t y);
|
||||
VirtualCoords coords;
|
||||
|
||||
int16_t virtualResX;
|
||||
int16_t virtualResY;
|
||||
|
||||
int16_t _virtualResX; ///< Display width as modified by current rotation
|
||||
int16_t _virtualResY; ///< Display height as modified by current rotation
|
||||
|
||||
int16_t vmodule_rows;
|
||||
int16_t vmodule_cols;
|
||||
|
||||
int16_t panelResX;
|
||||
int16_t panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
int16_t dmaResX; // The width of the chain in pixels (as the DMA engine sees it)
|
||||
|
||||
int _rotate = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
int _scale_factor = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
}; // end Class header
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -146,202 +171,368 @@ protected:
|
|||
* Updates the private class member variable 'coords', so no need to use the return value.
|
||||
* Not thread safe, but not a concern for ESP32 sketch anyway... I think.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
inline VirtualCoords VirtualMatrixPanel::getCoords(int16_t &x, int16_t &y)
|
||||
inline VirtualCoords VirtualMatrixPanel::getCoords(int16_t virt_x, int16_t virt_y)
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Serial.println("Called Base.");
|
||||
coords.x = coords.y = -1; // By defalt use an invalid co-ordinates that will be rejected by updateMatrixDMABuffer
|
||||
|
||||
#if !defined NO_GFX
|
||||
// I don't give any support if Adafruit GFX isn't being used.
|
||||
|
||||
if (virt_x < 0 || virt_x >= _width || virt_y < 0 || virt_y >= _height) // _width and _height are defined in the adafruit constructor
|
||||
{ // Co-ordinates go from 0 to X-1 remember! otherwise they are out of range!
|
||||
coords.x = coords.y = -1; // By defalt use an invalid co-ordinates that will be rejected by updateMatrixDMABuffer
|
||||
return coords;
|
||||
}
|
||||
#else
|
||||
|
||||
if (virt_x < 0 || virt_x >= _virtualResX || virt_y < 0 || virt_y >= _virtualResY) // _width and _height are defined in the adafruit constructor
|
||||
{ // Co-ordinates go from 0 to X-1 remember! otherwise they are out of range!
|
||||
coords.x = coords.y = -1; // By defalt use an invalid co-ordinates that will be rejected by updateMatrixDMABuffer
|
||||
return coords;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// Do we want to rotate?
|
||||
switch (_rotate) {
|
||||
case 0: //no rotation, do nothing
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case (1): //90 degree rotation
|
||||
{
|
||||
int16_t temp_x = virt_x;
|
||||
virt_x = virt_y;
|
||||
virt_y = virtualResY - 1 - temp_x;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Do we want to rotate?
|
||||
if (_rotate)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int16_t temp_x = x;
|
||||
x = y;
|
||||
y = virtualResY - 1 - temp_x;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case (2): //180 rotation
|
||||
{
|
||||
virt_x = virtualResX - 1 - virt_x;
|
||||
virt_y = virtualResY - 1 - virt_y;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case (3): //270 rotation
|
||||
{
|
||||
int16_t temp_x = virt_x;
|
||||
virt_x = virtualResX - 1 - virt_y;
|
||||
virt_y = temp_x;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int row = (virt_y / panelResY); // 0 indexed
|
||||
switch (panel_chain_type)
|
||||
{
|
||||
case (CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN):
|
||||
{
|
||||
if ((row % 2) == 1)
|
||||
{ // upside down panel
|
||||
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 1, row %d ", row);
|
||||
|
||||
// reversed for the row
|
||||
coords.x = dmaResX - virt_x - (row * virtualResX);
|
||||
|
||||
// y co-ord inverted within the panel
|
||||
coords.y = panelResY - 1 - (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row + 1)) * virtualResX) + virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case (CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN_ZZ):
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Right side up. Starting from top right all the way down.
|
||||
// Connected in a Zig Zag manner = some long ass cables being used potentially
|
||||
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row + 1)) * virtualResX) + virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case (CHAIN_TOP_LEFT_DOWN): // OK -> modulus opposite of CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN
|
||||
{
|
||||
if ((row % 2) == 0)
|
||||
{ // reversed panel
|
||||
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 1, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = dmaResX - virt_x - (row * virtualResX);
|
||||
|
||||
// y co-ord inverted within the panel
|
||||
coords.y = panelResY - 1 - (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row + 1)) * virtualResX) + virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case (CHAIN_TOP_LEFT_DOWN_ZZ):
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row + 1)) * virtualResX) + virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case (CHAIN_BOTTOM_LEFT_UP): //
|
||||
{
|
||||
row = vmodule_rows - row - 1;
|
||||
|
||||
if ((row % 2) == 1)
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 1, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row + 1)) * virtualResX) + virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{ // inverted panel
|
||||
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = dmaResX - (row * virtualResX) - virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = panelResY - 1 - (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case (CHAIN_BOTTOM_LEFT_UP_ZZ): //
|
||||
{
|
||||
row = vmodule_rows - row - 1;
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 1, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row + 1)) * virtualResX) + virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case (CHAIN_BOTTOM_RIGHT_UP): // OK -> modulus opposite of CHAIN_BOTTOM_LEFT_UP
|
||||
{
|
||||
row = vmodule_rows - row - 1;
|
||||
|
||||
if ((row % 2) == 0)
|
||||
{ // right side up
|
||||
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 1, row %d ", row);
|
||||
// refersed for the row
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row + 1)) * virtualResX) + virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{ // inverted panel
|
||||
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = dmaResX - (row * virtualResX) - virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = panelResY - 1 - (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case (CHAIN_BOTTOM_RIGHT_UP_ZZ):
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Right side up. Starting bottom right all the way up.
|
||||
// Connected in a Zig Zag manner = some long ass cables being used potentially
|
||||
|
||||
row = vmodule_rows - row - 1;
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row + 1)) * virtualResX) + virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
// Q: 1 row!? Why?
|
||||
// A: In cases people are only using virtual matrix panel for panels of non-standard scan rates.
|
||||
default:
|
||||
coords.x = virt_x; coords.y = virt_y;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
} // end switch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* START: Pixel remapping AGAIN to convert TWO parallel scanline output that the
|
||||
* the underlying hardware library is designed for (because
|
||||
* there's only 2 x RGB pins... and convert this to 1/4 or something
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
if ((panel_scan_rate == FOUR_SCAN_32PX_HIGH) || (panel_scan_rate == FOUR_SCAN_64PX_HIGH))
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
if (panel_scan_rate == FOUR_SCAN_64PX_HIGH)
|
||||
{
|
||||
// https://github.com/mrfaptastic/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-DMA/issues/345#issuecomment-1510401192
|
||||
if ((virt_y & 8) != ((virt_y & 16) >> 1)) { virt_y = (virt_y & 0b11000) ^ 0b11000 + (virt_y & 0b11100111); }
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Convert Real World 'VirtualMatrixPanel' co-ordinates (i.e. Real World pixel you're looking at
|
||||
on the panel or chain of panels, per the chaining configuration) to a 1/8 panels
|
||||
double 'stretched' and 'squished' coordinates which is what needs to be sent from the
|
||||
DMA buffer.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: Look at the FourScanPanel example code and you'll see that the DMA buffer is setup
|
||||
as if the panel is 2 * W and 0.5 * H !
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
if ((virt_y & 8) == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x += ((coords.x / panelResX) + 1) * panelResX; // 1st, 3rd 'block' of 8 rows of pixels, offset by panel width in DMA buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x += (coords.x / panelResX) * panelResX; // 2nd, 4th 'block' of 8 rows of pixels, offset by panel width in DMA buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// http://cpp.sh/4ak5u
|
||||
// Real number of DMA y rows is half reality
|
||||
// coords.y = (y / 16)*8 + (y & 0b00000111);
|
||||
coords.y = (virt_y >> 4) * 8 + (virt_y & 0b00000111);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (panel_scan_rate == FOUR_SCAN_16PX_HIGH)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if ((virt_y & 8) == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x += (panelResX >> 2) * (((coords.x & 0xFFF0) >> 4) + 1); // 1st, 3rd 'block' of 8 rows of pixels, offset by panel width in DMA buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x += (panelResX >> 2) * (((coords.x & 0xFFF0) >> 4)); // 2nd, 4th 'block' of 8 rows of pixels, offset by panel width in DMA buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (virt_y < 32)
|
||||
coords.y = (virt_y >> 4) * 8 + (virt_y & 0b00000111);
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.y = ((virt_y - 32) >> 4) * 8 + (virt_y & 0b00000111);
|
||||
coords.x += 256;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (x < 0 || x >= virtualResX || y < 0 || y >= virtualResY)
|
||||
{ // Co-ordinates go from 0 to X-1 remember! otherwise they are out of range!
|
||||
// Serial.printf("VirtualMatrixPanel::getCoords(): Invalid virtual display coordinate. x,y: %d, %d\r\n", x, y);
|
||||
return coords;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Stupidity check
|
||||
if ((vmodule_rows == 1) && (vmodule_cols == 1)) // single panel...
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x = x;
|
||||
coords.y = y;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
uint8_t row = (y / panelResY) + 1; // a non indexed 0 row number
|
||||
if ((_s_chain_party && !_chain_top_down && (row % 2 == 0)) // serpentine vertically stacked chain starting from bottom row (i.e. ESP closest to ground), upwards
|
||||
||
|
||||
(_s_chain_party && _chain_top_down && (row % 2 != 0)) // serpentine vertically stacked chain starting from the sky downwards
|
||||
)
|
||||
{
|
||||
// First portion gets you to the correct offset for the row you need
|
||||
// Second portion inverts the x on the row
|
||||
coords.x = ((y / panelResY) * (virtualResX)) + (virtualResX - x) - 1;
|
||||
|
||||
// inverts the y the row
|
||||
coords.y = panelResY - 1 - (y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Normal chain pixel co-ordinate
|
||||
coords.x = x + ((y / panelResY) * (virtualResX));
|
||||
coords.y = y % panelResY;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Reverse co-ordinates if panel chain from ESP starts from the TOP RIGHT
|
||||
if (_chain_top_down)
|
||||
{
|
||||
/*
|
||||
const HUB75_I2S_CFG _cfg = this->display->getCfg();
|
||||
coords.x = (_cfg.mx_width * _cfg.chain_length - 1) - coords.x;
|
||||
coords.y = (_cfg.mx_height-1) - coords.y;
|
||||
*/
|
||||
coords.x = (dmaResX - 1) - coords.x;
|
||||
coords.y = (panelResY - 1) - coords.y;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* START: Pixel remapping AGAIN to convert TWO parallel scanline output that the
|
||||
* the underlying hardware library is designed for (because
|
||||
* there's only 2 x RGB pins... and convert this to 1/4 or something
|
||||
*/
|
||||
if (_panelScanRate == FOUR_SCAN_32PX_HIGH)
|
||||
{
|
||||
/* Convert Real World 'VirtualMatrixPanel' co-ordinates (i.e. Real World pixel you're looking at
|
||||
on the panel or chain of panels, per the chaining configuration) to a 1/8 panels
|
||||
double 'stretched' and 'squished' coordinates which is what needs to be sent from the
|
||||
DMA buffer.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: Look at the FourScanPanel example code and you'll see that the DMA buffer is setup
|
||||
as if the panel is 2 * W and 0.5 * H !
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Serial.print("VirtualMatrixPanel Mapping ("); Serial.print(x, DEC); Serial.print(","); Serial.print(y, DEC); Serial.print(") ");
|
||||
// to
|
||||
Serial.print("to ("); Serial.print(coords.x, DEC); Serial.print(","); Serial.print(coords.y, DEC); Serial.println(") ");
|
||||
*/
|
||||
if ((y & 8) == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x += ((coords.x / panelResX) + 1) * panelResX; // 1st, 3rd 'block' of 8 rows of pixels, offset by panel width in DMA buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x += (coords.x / panelResX) * panelResX; // 2nd, 4th 'block' of 8 rows of pixels, offset by panel width in DMA buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// http://cpp.sh/4ak5u
|
||||
// Real number of DMA y rows is half reality
|
||||
// coords.y = (y / 16)*8 + (y & 0b00000111);
|
||||
coords.y = (y >> 4) * 8 + (y & 0b00000111);
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
Serial.print("OneEightScanPanel Mapping ("); Serial.print(x, DEC); Serial.print(","); Serial.print(y, DEC); Serial.print(") ");
|
||||
// to
|
||||
Serial.print("to ("); Serial.print(coords.x, DEC); Serial.print(","); Serial.print(coords.y, DEC); Serial.println(") ");
|
||||
*/
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (_panelScanRate == FOUR_SCAN_16PX_HIGH)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if ((y & 8) == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x += (panelResX >> 2) * (((coords.x & 0xFFF0) >> 4) + 1); // 1st, 3rd 'block' of 8 rows of pixels, offset by panel width in DMA buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x += (panelResX >> 2) * (((coords.x & 0xFFF0) >> 4)); // 2nd, 4th 'block' of 8 rows of pixels, offset by panel width in DMA buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (y < 32)
|
||||
coords.y = (y >> 4) * 8 + (y & 0b00000111);
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.y = ((y - 32) >> 4) * 8 + (y & 0b00000111);
|
||||
coords.x += 256;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Serial.print("Mapping to x: "); Serial.print(coords.x, DEC); Serial.print(", y: "); Serial.println(coords.y, DEC);
|
||||
return coords;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline void VirtualMatrixPanel::drawPixel(int16_t x, int16_t y, uint16_t color)
|
||||
{ // adafruit virtual void override
|
||||
getCoords(x, y);
|
||||
this->display->drawPixel(coords.x, coords.y, color);
|
||||
|
||||
if (_scale_factor > 1) // only from 2 and beyond
|
||||
{
|
||||
int16_t scaled_x_start_pos = x * _scale_factor;
|
||||
int16_t scaled_y_start_pos = y * _scale_factor;
|
||||
|
||||
for (int16_t x = 0; x < _scale_factor; x++) {
|
||||
for (int16_t y = 0; y < _scale_factor; y++) {
|
||||
VirtualCoords result = this->getCoords(scaled_x_start_pos+x, scaled_y_start_pos+y);
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Requested virtual x,y coord (%d, %d), got phyical chain coord of (%d,%d)\n", x,y, coords.x, coords.y);
|
||||
this->display->drawPixel(result.x, result.y, color);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
this->getCoords(x, y);
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Requested virtual x,y coord (%d, %d), got phyical chain coord of (%d,%d)\n", x,y, coords.x, coords.y);
|
||||
this->display->drawPixel(coords.x, coords.y, color);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline void VirtualMatrixPanel::fillScreen(uint16_t color)
|
||||
{ // adafruit virtual void override
|
||||
this->display->fillScreen(color);
|
||||
this->display->fillScreen(color);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline void VirtualMatrixPanel::fillScreenRGB888(uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b)
|
||||
{
|
||||
this->display->fillScreenRGB888(r, g, b);
|
||||
this->display->fillScreenRGB888(r, g, b);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline void VirtualMatrixPanel::drawPixelRGB888(int16_t x, int16_t y, uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b)
|
||||
{
|
||||
getCoords(x, y);
|
||||
this->display->drawPixelRGB888(coords.x, coords.y, r, g, b);
|
||||
this->getCoords(x, y);
|
||||
this->display->drawPixelRGB888(coords.x, coords.y, r, g, b);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef USE_GFX_ROOT
|
||||
// Support for CRGB values provided via FastLED
|
||||
inline void VirtualMatrixPanel::drawPixel(int16_t x, int16_t y, CRGB color)
|
||||
{
|
||||
getCoords(x, y);
|
||||
this->display->drawPixel(coords.x, coords.y, color);
|
||||
this->getCoords(x, y);
|
||||
this->display->drawPixel(coords.x, coords.y, color);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline void VirtualMatrixPanel::fillScreen(CRGB color)
|
||||
{
|
||||
this->display->fillScreen(color);
|
||||
this->display->fillScreen(color);
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
inline void VirtualMatrixPanel::setRotate(bool rotate)
|
||||
inline void VirtualMatrixPanel::setRotation(int rotate)
|
||||
{
|
||||
_rotate = rotate;
|
||||
if(rotate < 4 && rotate >= 0)
|
||||
_rotate = rotate;
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef NO_GFX
|
||||
// We don't support rotation by degrees.
|
||||
if (rotate)
|
||||
{
|
||||
setRotation(1);
|
||||
// Change the _width and _height variables used by the underlying adafruit gfx library.
|
||||
// Actual pixel rotation / mapping is done in the getCoords function.
|
||||
rotation = (rotate & 3);
|
||||
switch (rotation) {
|
||||
case 0: // nothing
|
||||
case 2: // 180
|
||||
_virtualResX = virtualResX;
|
||||
_virtualResY = virtualResY;
|
||||
|
||||
#if !defined NO_GFX
|
||||
_width = virtualResX; // adafruit base class
|
||||
_height = virtualResY; // adafruit base class
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case 1:
|
||||
case 3:
|
||||
_virtualResX = virtualResY;
|
||||
_virtualResY = virtualResX;
|
||||
|
||||
#if !defined NO_GFX
|
||||
_width = virtualResY; // adafruit base class
|
||||
_height = virtualResX; // adafruit base class
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
setRotation(0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline void VirtualMatrixPanel::setPhysicalPanelScanRate(PANEL_SCAN_RATE rate)
|
||||
{
|
||||
_panelScanRate = rate;
|
||||
panel_scan_rate = rate;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline void VirtualMatrixPanel::setZoomFactor(int scale)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(scale < 5 && scale > 0)
|
||||
_scale_factor = scale;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef NO_GFX
|
||||
inline void VirtualMatrixPanel::drawDisplayTest()
|
||||
{
|
||||
this->display->setFont(&FreeSansBold12pt7b);
|
||||
this->display->setTextColor(this->display->color565(255, 255, 0));
|
||||
this->display->setTextSize(1);
|
||||
// Write to the underlying panels only via the dma_display instance.
|
||||
this->display->setFont(&FreeSansBold12pt7b);
|
||||
this->display->setTextColor(this->display->color565(255, 255, 0));
|
||||
this->display->setTextSize(1);
|
||||
|
||||
for (int panel = 0; panel < vmodule_cols * vmodule_rows; panel++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int top_left_x = (panel == 0) ? 0 : (panel * panelResX);
|
||||
this->display->drawRect(top_left_x, 0, panelResX, panelResY, this->display->color565(0, 255, 0));
|
||||
this->display->setCursor(panel * panelResX, panelResY - 3);
|
||||
this->display->print((vmodule_cols * vmodule_rows) - panel);
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int panel = 0; panel < vmodule_cols * vmodule_rows; panel++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int top_left_x = (panel == 0) ? 0 : (panel * panelResX);
|
||||
this->display->drawRect(top_left_x, 0, panelResX, panelResY, this->display->color565(0, 255, 0));
|
||||
this->display->setCursor((panel * panelResX) + 2, panelResY - 4);
|
||||
this->display->print((vmodule_cols * vmodule_rows) - panel);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -28,54 +28,35 @@ Modified heavily for the ESP32 HUB75 DMA library by:
|
|||
#include <driver/periph_ctrl.h>
|
||||
#include <soc/gpio_sig_map.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#include <Arduino.h> // Need to make sure thi is uncommented to get ESP_LOG output on (Arduino) Serial output!!!!
|
||||
#if defined (ARDUINO_ARCH_ESP32)
|
||||
#include <Arduino.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include <esp_err.h>
|
||||
#include <esp_log.h>
|
||||
|
||||
// Get CPU freq function.
|
||||
#include <soc/rtc.h>
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
|
||||
callback shiftCompleteCallback;
|
||||
void setShiftCompleteCallback(callback f) {
|
||||
shiftCompleteCallback = f;
|
||||
}
|
||||
volatile bool previousBufferFree = true;
|
||||
|
||||
volatile int previousBufferOutputLoopCount = 0;
|
||||
volatile bool previousBufferFree = true;
|
||||
|
||||
static void IRAM_ATTR irq_hndlr(void* arg) { // if we use I2S1 (default)
|
||||
|
||||
SET_PERI_REG_BITS(I2S_INT_CLR_REG(ESP32_I2S_DEVICE), I2S_OUT_EOF_INT_CLR_V, 1, I2S_OUT_EOF_INT_CLR_S);
|
||||
|
||||
previousBufferFree = true;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
} // end irq_hndlr
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
volatile int DRAM_ATTR active_dma_buffer_output_count = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
void IRAM_ATTR irq_hndlr(void* arg) {
|
||||
static void IRAM_ATTR i2s_isr(void* arg) {
|
||||
|
||||
// From original Sprite_TM Code
|
||||
//REG_WRITE(I2S_INT_CLR_REG(1), (REG_READ(I2S_INT_RAW_REG(1)) & 0xffffffc0) | 0x3f);
|
||||
|
||||
// Clear flag so we can get retriggered
|
||||
SET_PERI_REG_BITS(I2S_INT_CLR_REG(ESP32_I2S_DEVICE), I2S_OUT_EOF_INT_CLR_V, 1, I2S_OUT_EOF_INT_CLR_S);
|
||||
|
||||
// at this point, the previously active buffer is free, go ahead and write to it
|
||||
previousBufferFree = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
active_dma_buffer_output_count++;
|
||||
bool DRAM_ATTR i2s_parallel_is_previous_buffer_free() {
|
||||
return previousBufferFree;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
if ( active_dma_buffer_output_count++ )
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Disable DMA chain EOF interrupt until next requested flipbuffer.
|
||||
// Otherwise we're needlessly generating interrupts we don't care about.
|
||||
//SET_PERI_REG_BITS(I2S_INT_ENA_REG(ESP32_I2S_DEVICE), I2S_OUT_EOF_INT_ENA_V, 0, I2S_OUT_EOF_INT_ENA_S);
|
||||
active_dma_buffer_output_count = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
} // end irq_hndlr
|
||||
|
||||
// Static
|
||||
i2s_dev_t* getDev()
|
||||
|
|
@ -221,22 +202,6 @@ static void IRAM_ATTR irq_hndlr(void* arg) { // if we use I2S1 (default)
|
|||
ESP_LOGD("ESP32/S2", "Requested output clock frequency: %d Mhz", (freq/1000000));
|
||||
|
||||
// What is the current CPU frequency?
|
||||
/*
|
||||
rtc_cpu_freq_config_t conf;
|
||||
rtc_clk_cpu_freq_get_config(&conf);
|
||||
auto source_freq = conf.source_freq_mhz;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ESP_LOGD("ESP32/S2", "PLL (source) frequency: %d", source_freq);
|
||||
ESP_LOGD("ESP32/S2", "CPU frequency: %d", conf.freq_mhz);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
if(_div_num < 2 || _div_num > 16) {
|
||||
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
// Calculate clock divider for ESP32-S2
|
||||
#if defined (CONFIG_IDF_TARGET_ESP32S2)
|
||||
|
|
@ -303,7 +268,7 @@ static void IRAM_ATTR irq_hndlr(void* arg) { // if we use I2S1 (default)
|
|||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
output_freq = output_freq + 0; // work around arudino 'unused var' issue if debug isn't enabled.
|
||||
output_freq = output_freq + 0; // work around arudino 'unused var' issue if debug isn't enabled.
|
||||
ESP_LOGI("ESP32/S2", "Output frequency is %ld Mhz??", (output_freq/1000000/i2s_parallel_get_memory_width(ESP32_I2S_DEVICE, 16)));
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -411,34 +376,23 @@ static void IRAM_ATTR irq_hndlr(void* arg) { // if we use I2S1 (default)
|
|||
dev->conf1.tx_stop_en = 0;
|
||||
dev->timing.val = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// If we have double buffering, then allocate an interrupt service routine function
|
||||
// that can be used for I2S0/I2S1 created interrupts.
|
||||
|
||||
// Setup I2S Interrupt
|
||||
SET_PERI_REG_BITS(I2S_INT_ENA_REG(ESP32_I2S_DEVICE), I2S_OUT_EOF_INT_ENA_V, 1, I2S_OUT_EOF_INT_ENA_S);
|
||||
|
||||
// Allocate a level 1 intterupt: lowest priority, as ISR isn't urgent and may take a long time to complete
|
||||
esp_intr_alloc(irq_source, (int)(ESP_INTR_FLAG_IRAM | ESP_INTR_FLAG_LEVEL1), i2s_isr, NULL, NULL);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* If we have double buffering, then allocate an interrupt service routine function
|
||||
* that can be used for I2S0/I2S1 created interrupts.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
if (_double_dma_buffer) {
|
||||
|
||||
// Get ISR setup
|
||||
esp_err_t err = esp_intr_alloc(irq_source,
|
||||
(int)(ESP_INTR_FLAG_IRAM | ESP_INTR_FLAG_LEVEL1),
|
||||
irq_hndlr, NULL, NULL);
|
||||
|
||||
if(err) {
|
||||
ESP_LOGE("ESP32/S2", "init() Failed to setup interrupt request handeler.");
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Don't do this here. Don't enable just yet.
|
||||
// dev->int_ena.out_eof = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined (CONFIG_IDF_TARGET_ESP32S2)
|
||||
ESP_LOGD("ESP32-S2", "init() GPIO and clock configuration set for ESP32-S2");
|
||||
#else
|
||||
ESP_LOGD("ESP32-ORIG", "init() GPIO and clock configuration set for ESP32");
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -490,7 +444,7 @@ static void IRAM_ATTR irq_hndlr(void* arg) { // if we use I2S1 (default)
|
|||
|
||||
ESP_LOGD("ESP32/S2", "Allocating the second buffer (double buffer enabled).");
|
||||
|
||||
_dmadesc_b= (HUB75_DMA_DESCRIPTOR_T*)heap_caps_malloc(sizeof(HUB75_DMA_DESCRIPTOR_T) * len, MALLOC_CAP_DMA);
|
||||
_dmadesc_b = (HUB75_DMA_DESCRIPTOR_T*)heap_caps_malloc(sizeof(HUB75_DMA_DESCRIPTOR_T) * len, MALLOC_CAP_DMA);
|
||||
|
||||
if (_dmadesc_b == nullptr)
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
|
@ -611,20 +565,15 @@ static void IRAM_ATTR irq_hndlr(void* arg) { // if we use I2S1 (default)
|
|||
} // end
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void Bus_Parallel16::flip_dma_output_buffer(int ¤t_back_buffer_id) // pass by reference so we can change in main matrixpanel class
|
||||
void Bus_Parallel16::flip_dma_output_buffer(int buffer_id) // pass by reference so we can change in main matrixpanel class
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
// Setup interrupt handler which is focussed only on the (page 322 of Tech. Ref. Manual)
|
||||
// "I2S_OUT_EOF_INT: Triggered when rxlink has finished sending a packet" (when dma linked list with eof = 1 is hit)
|
||||
//_dev->int_ena.out_eof = 1;
|
||||
_dev->int_ena.out_eof = 1; // enable interrupt
|
||||
|
||||
if ( current_back_buffer_id == 1) {
|
||||
|
||||
if ( buffer_id == 1) {
|
||||
|
||||
_dmadesc_a[_dmadesc_last].qe.stqe_next = &_dmadesc_b[0]; // Start sending out _dmadesc_b (or buffer 1)
|
||||
|
||||
active_dma_buffer_output_count = 0;
|
||||
while (!active_dma_buffer_output_count) {}
|
||||
_dmadesc_a[_dmadesc_last].qe.stqe_next = &_dmadesc_b[0]; // Start sending out _dmadesc_b (or buffer 1)
|
||||
|
||||
//fix _dmadesc_ loop issue #407
|
||||
//need to connect the up comming _dmadesc_ not the old one
|
||||
|
|
@ -633,17 +582,16 @@ static void IRAM_ATTR irq_hndlr(void* arg) { // if we use I2S1 (default)
|
|||
} else {
|
||||
|
||||
_dmadesc_b[_dmadesc_last].qe.stqe_next = &_dmadesc_a[0];
|
||||
|
||||
active_dma_buffer_output_count = 0;
|
||||
while (!active_dma_buffer_output_count) {}
|
||||
|
||||
_dmadesc_a[_dmadesc_last].qe.stqe_next = &_dmadesc_a[0];
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
current_back_buffer_id ^= 1;
|
||||
|
||||
// Disable intterupt
|
||||
_dev->int_ena.out_eof = 0;
|
||||
previousBufferFree = false;
|
||||
//while (i2s_parallel_is_previous_buffer_free() == false) {}
|
||||
while (!previousBufferFree);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
} // end flip
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -49,13 +49,16 @@ Contributors:
|
|||
|
||||
#define DMA_MAX (4096-4)
|
||||
|
||||
#ifndef ESP32_I2S_DEVICE
|
||||
#define ESP32_I2S_DEVICE I2S_NUM_0
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
// The type used for this SoC
|
||||
#define HUB75_DMA_DESCRIPTOR_T lldesc_t
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#if defined (CONFIG_IDF_TARGET_ESP32S2)
|
||||
#define ESP32_I2S_DEVICE I2S_NUM_0
|
||||
#else
|
||||
#define ESP32_I2S_DEVICE I2S_NUM_1
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
void IRAM_ATTR irq_hndlr(void* arg);
|
||||
|
|
@ -119,7 +122,7 @@ i2s_dev_t* getDev();
|
|||
void dma_transfer_start();
|
||||
void dma_transfer_stop();
|
||||
|
||||
void flip_dma_output_buffer(int ¤t_back_buffer_id);
|
||||
void flip_dma_output_buffer(int buffer_id);
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
|||
/*
|
||||
/*********************************************************************************************
|
||||
Simple example of using the ESP32-S3's LCD peripheral for general-purpose
|
||||
(non-LCD) parallel data output with DMA. Connect 8 LEDs (or logic analyzer),
|
||||
cycles through a pattern among them at about 1 Hz.
|
||||
|
|
@ -15,33 +15,30 @@
|
|||
|
||||
PLEASE SUPPORT THEM!
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
********************************************************************************************/
|
||||
#if __has_include (<hal/lcd_ll.h>)
|
||||
// Stop compile errors: /src/platforms/esp32s3/gdma_lcd_parallel16.hpp:64:10: fatal error: hal/lcd_ll.h: No such file or directory
|
||||
|
||||
#ifdef ARDUINO_ARCH_ESP32
|
||||
#include <Arduino.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
#ifdef ARDUINO_ARCH_ESP32
|
||||
#include <Arduino.h>
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
|
||||
#include "gdma_lcd_parallel16.hpp"
|
||||
#include "esp_attr.h"
|
||||
|
||||
//#if (CORE_DEBUG_LEVEL > ARDUHAL_LOG_LEVEL_NONE) || (ARDUHAL_LOG_LEVEL > ARDUHAL_LOG_LEVEL_NONE)
|
||||
// static const char* TAG = "gdma_lcd_parallel16";
|
||||
//#endif
|
||||
|
||||
//static int _dmadesc_a_idx = 0;
|
||||
//static int _dmadesc_b_idx = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
dma_descriptor_t desc; // DMA descriptor for testing
|
||||
/*
|
||||
dma_descriptor_t desc; // DMA descriptor for testing
|
||||
|
||||
uint8_t data[8][312]; // Transmit buffer (2496 bytes total)
|
||||
uint16_t* dmabuff2;
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
DRAM_ATTR volatile bool previousBufferFree = true;
|
||||
|
||||
// End-of-DMA-transfer callback
|
||||
IRAM_ATTR bool dma_callback(gdma_channel_handle_t dma_chan,
|
||||
IRAM_ATTR bool gdma_on_trans_eof_callback(gdma_channel_handle_t dma_chan,
|
||||
gdma_event_data_t *event_data, void *user_data) {
|
||||
|
||||
// This DMA callback seems to trigger a moment before the last data has
|
||||
// issued (buffering between DMA & LCD peripheral?), so pause a moment
|
||||
// before stopping LCD data out. The ideal delay may depend on the LCD
|
||||
|
|
@ -53,7 +50,10 @@
|
|||
// the transfer has finished, and the same flag is set later to trigger
|
||||
// the next transfer.
|
||||
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_start = 0;
|
||||
//LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_start = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
previousBufferFree = true;
|
||||
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -83,7 +83,7 @@
|
|||
|
||||
// Reset LCD bus
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_reset = 1;
|
||||
esp_rom_delay_us(100);
|
||||
esp_rom_delay_us(1000);
|
||||
|
||||
// uint32_t lcd_clkm_div_num = ((160000000 + 1) / _cfg.bus_freq);
|
||||
// ESP_LOGI("", "Clock divider is %d", lcd_clkm_div_num);
|
||||
|
|
@ -99,45 +99,57 @@
|
|||
|
||||
// LCD_CAM_LCD_CLK_SEL Select LCD module source clock. 0: clock source is disabled. 1: XTAL_CLK. 2: PLL_D2_CLK. 3: PLL_F160M_CLK. (R/W)
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clk_sel = 3; // Use 160Mhz Clock Source
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_ck_out_edge = 0; // PCLK low in 1st half cycle
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_ck_idle_edge = 0; // PCLK low idle
|
||||
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clkcnt_n = 1; // Should never be zero
|
||||
|
||||
//LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clk_equ_sysclk = 0; // PCLK = CLK / (CLKCNT_N+1)
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clk_equ_sysclk = 1; // PCLK = CLK / 1 (... so 160Mhz still)
|
||||
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clkcnt_n = 1; // Should never be zero
|
||||
|
||||
//LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clk_equ_sysclk = 0; // PCLK = CLK / (CLKCNT_N+1)
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clk_equ_sysclk = 1; // PCLK = CLK / 1 (... so 160Mhz still)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if (_cfg.psram_clk_override) // fastest speed I can get PSRAM to work before nothing shows
|
||||
// https://esp32.com/viewtopic.php?f=5&t=24459&start=80#p94487
|
||||
/* Re: ESP32-S3 LCD and I2S FULL documentation
|
||||
* by ESP_Sprite » Fri Mar 25, 2022 2:06 am
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Are you sure you are staying within the limits of the psram throughput? If GDMA can't fetch data fast
|
||||
* enough it leads to corruption. Also keep in mind that worst case scenario, the gdma can only use half of
|
||||
* the bandwidth of the psram peripheral (as it's round-robin shared with the CPUs).
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
// Fastest speed I can get with Octoal PSRAM to work before nothing shows. Based on manual testing.
|
||||
// If using an ESP32-S3 with slower (half the bandwidth) Q-SPI (Quad), then the divisor will need to be '20' (8Mhz) which wil be flickery!
|
||||
if (_cfg.psram_clk_override)
|
||||
{
|
||||
ESP_LOGI("S3", "DMA buffer is on PSRAM. Limiting clockspeed....");
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clkm_div_num = 10; //16mhz is the fasted the Octal PSRAM can support it seems
|
||||
//LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clkm_div_num = 10; //16mhz is the fasted the Octal PSRAM can support it seems from faptastic's testing using an N8R8 variant (Octal SPI PSRAM).
|
||||
|
||||
// https://github.com/mrfaptastic/ESP32-HUB75-MatrixPanel-DMA/issues/441#issuecomment-1513631890
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clkm_div_num = 12; // 13Mhz is the fastest when the DMA memory is needed to service other peripherals as well.
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
auto freq = (_cfg.bus_freq);
|
||||
|
||||
auto _div_num = 8; // 20Mhz
|
||||
if (freq < 20000000L)
|
||||
{
|
||||
_div_num = 12; // 13Mhz
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (freq > 20000000L)
|
||||
{
|
||||
_div_num = 6; // 26Mhz --- likely to have noise without a good connection
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
auto freq = (_cfg.bus_freq);
|
||||
|
||||
auto _div_num = 8; // 20Mhz
|
||||
if (freq < 20000000L) {
|
||||
_div_num = 12; // 13Mhz
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (freq > 20000000L) {
|
||||
_div_num = 6; // 26Mhz --- likely to have noise without a good connection
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
//LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clkm_div_num = lcd_clkm_div_num;
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clkm_div_num = _div_num; //3;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
ESP_LOGI("S3", "Clock divider is %d", LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clkm_div_num);
|
||||
|
||||
ESP_LOGD("S3", "Resulting output clock frequency: %ld Mhz", (160000000L/LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clkm_div_num));
|
||||
ESP_LOGI("S3", "Clock divider is %d", LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clkm_div_num);
|
||||
ESP_LOGD("S3", "Resulting output clock frequency: %ld Mhz", (160000000L/LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clkm_div_num));
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clkm_div_a = 1; // 0/1 fractional divide
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_clock.lcd_clkm_div_b = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -150,13 +162,16 @@
|
|||
LCD_CAM.lcd_ctrl.lcd_rgb_mode_en = 0; // i8080 mode (not RGB)
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_rgb_yuv.lcd_conv_bypass = 0; // Disable RGB/YUV converter
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_misc.lcd_next_frame_en = 0; // Do NOT auto-frame
|
||||
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_misc.lcd_bk_en = 1; // https://esp32.com/viewtopic.php?t=24459&start=60#p91835
|
||||
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_data_dout_mode.val = 0; // No data delays
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_always_out_en = 1; // Enable 'always out' mode
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_8bits_order = 0; // Do not swap bytes
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_bit_order = 0; // Do not reverse bit order
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_2byte_en = 1; // 8-bit data mode
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_dummy = 0; // Dummy phase(s) @ LCD start
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_dummy_cyclelen = 0; // 1 dummy phase
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_dummy = 1; // Dummy phase(s) @ LCD start
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_dummy_cyclelen = 1; // 1+1 dummy phase
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_cmd = 0; // No command at LCD start
|
||||
// "Dummy phases" are initial LCD peripheral clock cycles before data
|
||||
// begins transmitting when requested. After much testing, determined
|
||||
|
|
@ -212,10 +227,11 @@
|
|||
// in a single DMA descriptor (max 4095 bytes). Large transfers would
|
||||
// require a linked list of descriptors, but here it's just one...
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
desc.dw0.owner = DMA_DESCRIPTOR_BUFFER_OWNER_DMA;
|
||||
desc.dw0.suc_eof = 0; // Last descriptor
|
||||
desc.next = &desc; // No linked list
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
// Remaining descriptor elements are initialized before each DMA transfer.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -236,38 +252,18 @@
|
|||
gdma_apply_strategy(dma_chan, &strategy_config);
|
||||
|
||||
gdma_transfer_ability_t ability = {
|
||||
.sram_trans_align = 4,
|
||||
.sram_trans_align = 32,
|
||||
.psram_trans_align = 64,
|
||||
};
|
||||
gdma_set_transfer_ability(dma_chan, &ability);
|
||||
|
||||
// Enable DMA transfer callback
|
||||
/*
|
||||
static gdma_tx_event_callbacks_t tx_cbs = {
|
||||
.on_trans_eof = dma_callback
|
||||
// .on_trans_eof is literally the only gdma tx event type available
|
||||
.on_trans_eof = gdma_on_trans_eof_callback
|
||||
};
|
||||
gdma_register_tx_event_callbacks(dma_chan, &tx_cbs, NULL);
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
// As mentioned earlier, the slowest clock we can get to the LCD
|
||||
// peripheral is 40 MHz / 250 / 64 = 2500 Hz. To make an even slower
|
||||
// bit pattern that's perceptible, we just repeat each value many
|
||||
// times over. The pattern here just counts through each of 8 bits
|
||||
// (each LED lights in sequence)...so to get this to repeat at about
|
||||
// 1 Hz, each LED is lit for 2500/8 or 312 cycles, hence the
|
||||
// data[8][312] declaration at the start of this code (it's not
|
||||
// precisely 1 Hz because reality is messy, but sufficient for demo).
|
||||
// In actual use, say controlling an LED matrix or NeoPixels, such
|
||||
// shenanigans aren't necessary, as these operate at multiple MHz
|
||||
// with much smaller clock dividers and can use 1 byte per datum.
|
||||
/*
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < (sizeof(data) / sizeof(data[0])); i++) { // 0 to 7
|
||||
for (int j = 0; j < sizeof(data[0]); j++) { // 0 to 311
|
||||
data[i][j] = 1 << i;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// This uses a busy loop to wait for each DMA transfer to complete...
|
||||
// but the whole point of DMA is that one's code can do other work in
|
||||
|
|
@ -277,36 +273,14 @@
|
|||
// After much experimentation, each of these steps is required to get
|
||||
// a clean start on the next LCD transfer:
|
||||
gdma_reset(dma_chan); // Reset DMA to known state
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_dout = 1; // Enable data out
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_update = 1; // Update registers
|
||||
esp_rom_delay_us(1000);
|
||||
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_dout = 1; // Enable data out
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_update = 1; // Update registers
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_misc.lcd_afifo_reset = 1; // Reset LCD TX FIFO
|
||||
|
||||
// This program happens to send the same data over and over...but,
|
||||
// if desired, one could fill the data buffer with a new bit pattern
|
||||
// here, or point to a completely different buffer each time through.
|
||||
// With two buffers, one can make best use of time by filling each
|
||||
// with new data before the busy loop above, alternating between them.
|
||||
|
||||
// Reset elements of DMA descriptor. Just one in this code, long
|
||||
// transfers would loop through a linked list.
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
desc.dw0.size = desc.dw0.length = sizeof(data);
|
||||
desc.buffer = dmabuff2; //data;
|
||||
desc.next = &desc;
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
//gdma_start(dma_chan, (intptr_t)&desc); // Start DMA w/updated descriptor(s)
|
||||
gdma_start(dma_chan, (intptr_t)&_dmadesc_a[0]); // Start DMA w/updated descriptor(s)
|
||||
esp_rom_delay_us(100); // Must 'bake' a moment before...
|
||||
LCD_CAM.lcd_user.lcd_start = 1; // Trigger LCD DMA transfer
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
return true; // no return val = illegal instruction
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -379,7 +353,8 @@
|
|||
{
|
||||
|
||||
_dmadesc_b[_dmadesc_b_idx].dw0.owner = DMA_DESCRIPTOR_BUFFER_OWNER_DMA;
|
||||
_dmadesc_b[_dmadesc_b_idx].dw0.suc_eof = 0;
|
||||
//_dmadesc_b[_dmadesc_b_idx].dw0.suc_eof = 0;
|
||||
_dmadesc_b[_dmadesc_b_idx].dw0.suc_eof = (_dmadesc_b_idx == (_dmadesc_count-1));
|
||||
_dmadesc_b[_dmadesc_b_idx].dw0.size = _dmadesc_b[_dmadesc_b_idx].dw0.length = size; //sizeof(data);
|
||||
_dmadesc_b[_dmadesc_b_idx].buffer = data; //data;
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -396,7 +371,7 @@
|
|||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if ( _dmadesc_a_idx >= _dmadesc_count)
|
||||
{
|
||||
ESP_LOGE("S3", "Attempted to create more DMA descriptors than allocated. Expecting max %" PRIu32 " descriptors.", _dmadesc_count);
|
||||
|
|
@ -404,7 +379,8 @@
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
_dmadesc_a[_dmadesc_a_idx].dw0.owner = DMA_DESCRIPTOR_BUFFER_OWNER_DMA;
|
||||
_dmadesc_a[_dmadesc_a_idx].dw0.suc_eof = 0;
|
||||
//_dmadesc_a[_dmadesc_a_idx].dw0.suc_eof = 0;
|
||||
_dmadesc_a[_dmadesc_a_idx].dw0.suc_eof = (_dmadesc_a_idx == (_dmadesc_count-1));
|
||||
_dmadesc_a[_dmadesc_a_idx].dw0.size = _dmadesc_a[_dmadesc_a_idx].dw0.length = size; //sizeof(data);
|
||||
_dmadesc_a[_dmadesc_a_idx].buffer = data; //data;
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -441,12 +417,12 @@
|
|||
} // end
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
void Bus_Parallel16::flip_dma_output_buffer(int ¤t_back_buffer_id)
|
||||
void Bus_Parallel16::flip_dma_output_buffer(int back_buffer_id)
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
// if ( _double_dma_buffer == false) return;
|
||||
|
||||
if ( current_back_buffer_id == 1) // change across to everything 'b''
|
||||
if ( back_buffer_id == 1) // change across to everything 'b''
|
||||
{
|
||||
_dmadesc_a[_dmadesc_count-1].next = (dma_descriptor_t *) &_dmadesc_b[0];
|
||||
_dmadesc_b[_dmadesc_count-1].next = (dma_descriptor_t *) &_dmadesc_b[0];
|
||||
|
|
@ -457,7 +433,14 @@
|
|||
_dmadesc_a[_dmadesc_count-1].next = (dma_descriptor_t *) &_dmadesc_a[0];
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
current_back_buffer_id ^= 1;
|
||||
//current_back_buffer_id ^= 1;
|
||||
|
||||
previousBufferFree = false;
|
||||
|
||||
//while (i2s_parallel_is_previous_buffer_free() == false) {}
|
||||
while (!previousBufferFree);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
} // end flip
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -147,7 +147,7 @@
|
|||
void dma_transfer_start();
|
||||
void dma_transfer_stop();
|
||||
|
||||
void flip_dma_output_buffer(int ¤t_back_buffer_id);
|
||||
void flip_dma_output_buffer(int back_buffer_id);
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -55,7 +55,8 @@ Modified heavily for the ESP32 HUB75 DMA library by:
|
|||
|
||||
// Assume an ESP32 (the original 2015 version)
|
||||
// Same include as ESP32S3
|
||||
#pragma message "Compiling for original ESP32 (released 2016)"
|
||||
//#pragma message "Compiling for original ESP32 (released 2016)"
|
||||
|
||||
#define ESP32_THE_ORIG 1
|
||||
//#include "esp32/esp32_i2s_parallel_dma.hpp"
|
||||
//#include "esp32/esp32_i2s_parallel_dma.h"
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
5
testing/README.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
|||
Sample app to simulate the VirtualMatrixPanel class for testing / optimisation, without having to test with physical panels.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
g++ -o myapp.exe virtual.cpp
|
||||
```
|
||||
189
testing/baseline.hpp
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,189 @@
|
|||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Calculate virtual->real co-ordinate mapping to underlying single chain of panels connected to ESP32.
|
||||
* Updates the private class member variable 'coords', so no need to use the return value.
|
||||
* Not thread safe, but not a concern for ESP32 sketch anyway... I think.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
// DO NOT CHANGE
|
||||
inline VirtualCoords VirtualMatrixPanelTest::getCoords_WorkingBaslineMarch2023(int16_t virt_x, int16_t virt_y)
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x = coords.y = -1; // By defalt use an invalid co-ordinates that will be rejected by updateMatrixDMABuffer
|
||||
|
||||
if (virt_x < 0 || virt_x >= virtualResX || virt_y < 0 || virt_y >= virtualResY)
|
||||
{ // Co-ordinates go from 0 to X-1 remember! otherwise they are out of range!
|
||||
return coords;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Do we want to rotate?
|
||||
if (_rotate)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int16_t temp_x = virt_x;
|
||||
virt_x = virt_y;
|
||||
virt_y = virtualResY - 1 - temp_x;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int row = (virt_y / panelResY); // 0 indexed
|
||||
switch(panel_chain_type)
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
case (CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN):
|
||||
{
|
||||
if ( (row % 2) == 1 )
|
||||
{ // upside down panel
|
||||
|
||||
//Serial.printf("Condition 1, row %d ", row);
|
||||
|
||||
// refersed for the row
|
||||
coords.x = dmaResX - virt_x - (row*virtualResX);
|
||||
|
||||
// y co-ord inverted within the panel
|
||||
coords.y = panelResY - 1 - (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
//Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row+1))*virtualResX)+virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = virt_y % panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
case (CHAIN_TOP_LEFT_DOWN): // OK -> modulus opposite of CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN
|
||||
{
|
||||
if ( (row % 2) == 0 )
|
||||
{ // refersed panel
|
||||
|
||||
//Serial.printf("Condition 1, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = dmaResX - virt_x - (row*virtualResX);
|
||||
|
||||
// y co-ord inverted within the panel
|
||||
coords.y = panelResY - 1 - (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
//Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row+1))*virtualResX)+virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = virt_y % panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
case (CHAIN_BOTTOM_LEFT_UP): //
|
||||
{
|
||||
row = vmodule_rows - row - 1;
|
||||
|
||||
if ( (row % 2) == 1 )
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 1, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row+1))*virtualResX)+virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = virt_y % panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{ // inverted panel
|
||||
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = dmaResX - (row*virtualResX) - virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = panelResY - 1 - (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case (CHAIN_BOTTOM_RIGHT_UP): // OK -> modulus opposite of CHAIN_BOTTOM_LEFT_UP
|
||||
{
|
||||
row = vmodule_rows - row - 1;
|
||||
|
||||
if ( (row % 2) == 0 )
|
||||
{ // right side up
|
||||
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 1, row %d ", row);
|
||||
// refersed for the row
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row+1))*virtualResX)+virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = virt_y % panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{ // inverted panel
|
||||
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = dmaResX - (row*virtualResX) - virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = panelResY - 1 - (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return coords;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
} // end switch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* START: Pixel remapping AGAIN to convert TWO parallel scanline output that the
|
||||
* the underlying hardware library is designed for (because
|
||||
* there's only 2 x RGB pins... and convert this to 1/4 or something
|
||||
*/
|
||||
if (panel_scan_rate == FOUR_SCAN_32PX_HIGH)
|
||||
{
|
||||
/* Convert Real World 'VirtualMatrixPanel' co-ordinates (i.e. Real World pixel you're looking at
|
||||
on the panel or chain of panels, per the chaining configuration) to a 1/8 panels
|
||||
double 'stretched' and 'squished' coordinates which is what needs to be sent from the
|
||||
DMA buffer.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: Look at the FourScanPanel example code and you'll see that the DMA buffer is setup
|
||||
as if the panel is 2 * W and 0.5 * H !
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
if ((virt_y & 8) == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x += ((coords.x / panelResX) + 1) * panelResX; // 1st, 3rd 'block' of 8 rows of pixels, offset by panel width in DMA buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x += (coords.x / panelResX) * panelResX; // 2nd, 4th 'block' of 8 rows of pixels, offset by panel width in DMA buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// http://cpp.sh/4ak5u
|
||||
// Real number of DMA y rows is half reality
|
||||
// coords.y = (y / 16)*8 + (y & 0b00000111);
|
||||
coords.y = (virt_y >> 4) * 8 + (virt_y & 0b00000111);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (panel_scan_rate == FOUR_SCAN_16PX_HIGH)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if ((virt_y & 8) == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x += (panelResX >> 2) * (((coords.x & 0xFFF0) >> 4) + 1); // 1st, 3rd 'block' of 8 rows of pixels, offset by panel width in DMA buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x += (panelResX >> 2) * (((coords.x & 0xFFF0) >> 4)); // 2nd, 4th 'block' of 8 rows of pixels, offset by panel width in DMA buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (virt_y < 32)
|
||||
coords.y = (virt_y >> 4) * 8 + (virt_y & 0b00000111);
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.y = ((virt_y - 32) >> 4) * 8 + (virt_y & 0b00000111);
|
||||
coords.x += 256;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return coords;
|
||||
}
|
||||
459
testing/virtual.cpp
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,459 @@
|
|||
#include <iostream>
|
||||
#include <string>
|
||||
#include <list>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
struct VirtualCoords
|
||||
{
|
||||
int16_t x;
|
||||
int16_t y;
|
||||
int16_t virt_row; // chain of panels row
|
||||
int16_t virt_col; // chain of panels col
|
||||
|
||||
VirtualCoords() : x(0), y(0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
enum PANEL_SCAN_RATE
|
||||
{
|
||||
NORMAL_TWO_SCAN, NORMAL_ONE_SIXTEEN, // treated as the same
|
||||
FOUR_SCAN_32PX_HIGH,
|
||||
FOUR_SCAN_16PX_HIGH
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Chaining approach... From the perspective of the DISPLAY / LED side of the chain of panels.
|
||||
enum PANEL_CHAIN_TYPE
|
||||
{
|
||||
CHAIN_TOP_LEFT_DOWN,
|
||||
CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN,
|
||||
CHAIN_BOTTOM_LEFT_UP,
|
||||
CHAIN_BOTTOM_RIGHT_UP,
|
||||
CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN_ZZ, /// ZigZag chaining. Might need a big ass cable to do this, all panels right way up.
|
||||
CHAIN_BOTTOM_RIGHT_UP_ZZ
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class VirtualMatrixPanelTest
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
VirtualMatrixPanelTest(int _vmodule_rows, int _vmodule_cols, int _panelResX, int _panelResY, PANEL_CHAIN_TYPE _panel_chain_type = CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN)
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
panelResX = _panelResX;
|
||||
panelResY = _panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
vmodule_rows = _vmodule_rows;
|
||||
vmodule_cols = _vmodule_cols;
|
||||
|
||||
virtualResX = vmodule_cols * _panelResX;
|
||||
virtualResY = vmodule_rows * _panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
dmaResX = panelResX * vmodule_rows * vmodule_cols;
|
||||
|
||||
panel_chain_type = _panel_chain_type;
|
||||
|
||||
/* Virtual Display width() and height() will return a real-world value. For example:
|
||||
* Virtual Display width: 128
|
||||
* Virtual Display height: 64
|
||||
*
|
||||
* So, not values that at 0 to X-1
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
coords.x = coords.y = -1; // By default use an invalid co-ordinates that will be rejected by updateMatrixDMABuffer
|
||||
|
||||
switch (panel_chain_type) {
|
||||
case CHAIN_TOP_LEFT_DOWN:
|
||||
chain_type_str = "CHAIN_TOP_LEFT_DOWN";
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN:
|
||||
chain_type_str = "CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN";
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN_ZZ:
|
||||
chain_type_str = "CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN_ZZ";
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case CHAIN_BOTTOM_RIGHT_UP:
|
||||
chain_type_str = "CHAIN_BOTTOM_RIGHT_UP";
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case CHAIN_BOTTOM_LEFT_UP:
|
||||
chain_type_str = "CHAIN_BOTTOM_LEFT_UP";
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
chain_type_str = "WTF!";
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
std::cout << "\n\n***************************************************************************\n";
|
||||
std::cout << "Chain type: " << chain_type_str << " ";
|
||||
std::printf("Testing chain of panels of %d rows, %d columns, %d px by %d px resolution. \n\n", vmodule_rows, vmodule_cols, panelResX, panelResX, panelResY);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// equivalent methods of the matrix library so it can be just swapped out.
|
||||
void drawPixel(int16_t x, int16_t y, int16_t expected_x, int16_t expected_y);
|
||||
|
||||
std::string chain_type_str = "UNKNOWN";
|
||||
|
||||
// Internal co-ord conversion function
|
||||
VirtualCoords getCoords_Dev(int16_t x, int16_t y);
|
||||
|
||||
VirtualCoords getCoords_WorkingBaslineMarch2023(int16_t x, int16_t y);
|
||||
|
||||
VirtualCoords coords;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
|
||||
int16_t virtualResX;
|
||||
int16_t virtualResY;
|
||||
|
||||
int16_t vmodule_rows;
|
||||
int16_t vmodule_cols;
|
||||
|
||||
int16_t panelResX;
|
||||
int16_t panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
int16_t dmaResX; // The width of the chain in pixels (as the DMA engine sees it)
|
||||
|
||||
PANEL_CHAIN_TYPE panel_chain_type;
|
||||
PANEL_SCAN_RATE panel_scan_rate = NORMAL_TWO_SCAN;
|
||||
|
||||
bool _rotate = false;
|
||||
|
||||
}; // end Class header
|
||||
|
||||
#include "baseline.hpp"
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* Development version for testing.
|
||||
*/
|
||||
inline VirtualCoords VirtualMatrixPanelTest::getCoords_Dev(int16_t virt_x, int16_t virt_y)
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x = coords.y = -1; // By defalt use an invalid co-ordinates that will be rejected by updateMatrixDMABuffer
|
||||
|
||||
if (virt_x < 0 || virt_x >= virtualResX || virt_y < 0 || virt_y >= virtualResY)
|
||||
{ // Co-ordinates go from 0 to X-1 remember! otherwise they are out of range!
|
||||
return coords;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Do we want to rotate?
|
||||
if (_rotate)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int16_t temp_x = virt_x;
|
||||
virt_x = virt_y;
|
||||
virt_y = virtualResY - 1 - temp_x;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
int row = (virt_y / panelResY); // 0 indexed
|
||||
switch(panel_chain_type)
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
case (CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN):
|
||||
{
|
||||
if ( (row % 2) == 1 )
|
||||
{ // upside down panel
|
||||
|
||||
//Serial.printf("Condition 1, row %d ", row);
|
||||
|
||||
// refersed for the row
|
||||
coords.x = dmaResX - virt_x - (row*virtualResX);
|
||||
|
||||
// y co-ord inverted within the panel
|
||||
coords.y = panelResY - 1 - (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
//Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row+1))*virtualResX)+virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = virt_y % panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
case (CHAIN_TOP_LEFT_DOWN): // OK -> modulus opposite of CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN
|
||||
{
|
||||
if ( (row % 2) == 0 )
|
||||
{ // refersed panel
|
||||
|
||||
//Serial.printf("Condition 1, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = dmaResX - virt_x - (row*virtualResX);
|
||||
|
||||
// y co-ord inverted within the panel
|
||||
coords.y = panelResY - 1 - (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
//Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row+1))*virtualResX)+virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = virt_y % panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
case (CHAIN_BOTTOM_LEFT_UP): //
|
||||
{
|
||||
row = vmodule_rows - row - 1;
|
||||
|
||||
if ( (row % 2) == 1 )
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 1, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row+1))*virtualResX)+virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = virt_y % panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{ // inverted panel
|
||||
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = dmaResX - (row*virtualResX) - virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = panelResY - 1 - (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case (CHAIN_BOTTOM_RIGHT_UP): // OK -> modulus opposite of CHAIN_BOTTOM_LEFT_UP
|
||||
{
|
||||
row = vmodule_rows - row - 1;
|
||||
|
||||
if ( (row % 2) == 0 )
|
||||
{ // right side up
|
||||
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 1, row %d ", row);
|
||||
// refersed for the row
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row+1))*virtualResX)+virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = virt_y % panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{ // inverted panel
|
||||
|
||||
// Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = dmaResX - (row*virtualResX) - virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = panelResY - 1 - (virt_y % panelResY);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
case CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN_ZZ:
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Right side up. Starting from top left all the way down.
|
||||
// Connected in a Zig Zag manner = some long ass cables being used potentially
|
||||
|
||||
//Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = ((vmodule_rows - (row+1))*virtualResX)+virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = virt_y % panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
case CHAIN_BOTTOM_RIGHT_UP_ZZ:
|
||||
{
|
||||
// Right side up. Starting from top left all the way down.
|
||||
// Connected in a Zig Zag manner = some long ass cables being used potentially
|
||||
|
||||
//Serial.printf("Condition 2, row %d ", row);
|
||||
coords.x = (row*virtualResX)+virt_x;
|
||||
coords.y = virt_y % panelResY;
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
default:
|
||||
return coords;
|
||||
break;
|
||||
|
||||
} // end switch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* START: Pixel remapping AGAIN to convert TWO parallel scanline output that the
|
||||
* the underlying hardware library is designed for (because
|
||||
* there's only 2 x RGB pins... and convert this to 1/4 or something
|
||||
*/
|
||||
if (panel_scan_rate == FOUR_SCAN_32PX_HIGH)
|
||||
{
|
||||
/* Convert Real World 'VirtualMatrixPanel' co-ordinates (i.e. Real World pixel you're looking at
|
||||
on the panel or chain of panels, per the chaining configuration) to a 1/8 panels
|
||||
double 'stretched' and 'squished' coordinates which is what needs to be sent from the
|
||||
DMA buffer.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: Look at the FourScanPanel example code and you'll see that the DMA buffer is setup
|
||||
as if the panel is 2 * W and 0.5 * H !
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
if ((virt_y & 8) == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x += ((coords.x / panelResX) + 1) * panelResX; // 1st, 3rd 'block' of 8 rows of pixels, offset by panel width in DMA buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x += (coords.x / panelResX) * panelResX; // 2nd, 4th 'block' of 8 rows of pixels, offset by panel width in DMA buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// http://cpp.sh/4ak5u
|
||||
// Real number of DMA y rows is half reality
|
||||
// coords.y = (y / 16)*8 + (y & 0b00000111);
|
||||
coords.y = (virt_y >> 4) * 8 + (virt_y & 0b00000111);
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (panel_scan_rate == FOUR_SCAN_16PX_HIGH)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if ((virt_y & 8) == 0)
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x += (panelResX >> 2) * (((coords.x & 0xFFF0) >> 4) + 1); // 1st, 3rd 'block' of 8 rows of pixels, offset by panel width in DMA buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.x += (panelResX >> 2) * (((coords.x & 0xFFF0) >> 4)); // 2nd, 4th 'block' of 8 rows of pixels, offset by panel width in DMA buffer
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (virt_y < 32)
|
||||
coords.y = (virt_y >> 4) * 8 + (virt_y & 0b00000111);
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
coords.y = ((virt_y - 32) >> 4) * 8 + (virt_y & 0b00000111);
|
||||
coords.x += 256;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return coords;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool check(VirtualCoords expected, VirtualCoords result, int x = -1, int y = -1)
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
if ( result.x != expected.x || result.y != expected.y )
|
||||
{
|
||||
std::printf("Requested (%d, %d) -> expecting physical (%d, %d) got (%d, %d).", x, y, expected.x, expected.y, result.x, result.y);
|
||||
std::cout << "\t *** FAIL ***\n ";
|
||||
std::cout << "\n";
|
||||
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
main(int argc, char* argv[])
|
||||
{
|
||||
std::cout << "Starting Testing...\n";
|
||||
|
||||
std::list <PANEL_CHAIN_TYPE> chain_t_test_list { CHAIN_TOP_LEFT_DOWN, CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN, CHAIN_BOTTOM_LEFT_UP, CHAIN_BOTTOM_RIGHT_UP };
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// Draw pixel at virtual position 70x, 70y =
|
||||
// x, y x, y
|
||||
|
||||
// x == horizontal
|
||||
// y = vert :-)
|
||||
|
||||
// 192 x 192 pixel virtual display
|
||||
int rows = 3;
|
||||
int cols = 3;
|
||||
int panel_width_x = 64;
|
||||
int panel_height_y = 64;
|
||||
|
||||
std::string panel_scan_type = "NORMAL_TWO_SCAN";
|
||||
|
||||
for (auto chain_t : chain_t_test_list) {
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
VirtualMatrixPanelTest test = VirtualMatrixPanelTest(rows,cols,panel_width_x,panel_height_y, chain_t);
|
||||
int pass_counter = 0;
|
||||
int fail_counter = 0;
|
||||
for (int16_t x = 0; x < panel_width_x*cols; x++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for (int16_t y = 0; y < panel_height_y*rows; y++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
VirtualCoords expected = test.getCoords_WorkingBaslineMarch2023(x,y);
|
||||
VirtualCoords result = test.getCoords_Dev(x,y);
|
||||
|
||||
bool chk_result = check(expected, result, x, y);
|
||||
|
||||
if ( chk_result )
|
||||
{
|
||||
fail_counter++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
pass_counter++;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if ( fail_counter > 0) {
|
||||
std::printf("ERROR: %d tests failed.\n", fail_counter);
|
||||
} else{
|
||||
std::printf("SUCCESS: %d coord tests passed.\n", pass_counter);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} // end chain type test list
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
std::cout << "Performing NON-SERPENTINE (ZIG ZAG) TEST";
|
||||
|
||||
rows = 3;
|
||||
cols = 1;
|
||||
panel_width_x = 64;
|
||||
panel_height_y = 64;
|
||||
|
||||
VirtualMatrixPanelTest test = VirtualMatrixPanelTest(rows,cols,panel_width_x,panel_height_y, CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN_ZZ);
|
||||
|
||||
// CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN_ZZ test 1
|
||||
// (x,y)
|
||||
VirtualCoords result = test.getCoords_Dev(0,0);
|
||||
VirtualCoords expected; expected.x = 64*2; expected.y = 0;
|
||||
std::printf("Expected physical (%d, %d) got (%d, %d).\n", expected.x, expected.y, result.x, result.y);
|
||||
|
||||
// CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN_ZZ test 2
|
||||
result = test.getCoords_Dev(10,64*3-1);
|
||||
expected.x = 10; expected.y = 63;
|
||||
std::printf("Expected physical (%d, %d) got (%d, %d).\n", expected.x, expected.y, result.x, result.y);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// CHAIN_TOP_RIGHT_DOWN_ZZ test 3
|
||||
result = test.getCoords_Dev(16,64*2-1);
|
||||
expected.x = 80; expected.y = 63;
|
||||
std::printf("Expected physical (%d, %d) got (%d, %d).\n", expected.x, expected.y, result.x, result.y);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// CHAIN_BOTTOM_RIGHT_UP_ZZ test 4
|
||||
result = test.getCoords_Dev(0,0);
|
||||
expected.x = 0; expected.y = 0;
|
||||
std::printf("Expected physical (%d, %d) got (%d, %d).\n", expected.x, expected.y, result.x, result.y);
|
||||
|
||||
// CHAIN_BOTTOM_RIGHT_UP_ZZ test 4
|
||||
result = test.getCoords_Dev(63,64);
|
||||
expected.x = 64*2-1; expected.y = 0;
|
||||
std::printf("Expected physical (%d, %d) got (%d, %d).\n", expected.x, expected.y, result.x, result.y);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
std::cout << "\n\n";
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||